A phase II, multicentre trial of decitabine in higher-risk chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
- PMID: 28607470
- PMCID: PMC5808077
- DOI: 10.1038/leu.2017.186
A phase II, multicentre trial of decitabine in higher-risk chronic myelomonocytic leukemia
Abstract
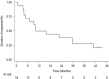
Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia (CMML) is a complex clonal hematological disorder classified among myelodysplastic (MDS)/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Prognosis is poor and there is a lack of effective treatments. The hypomethylating agent decitabine has shown activity against MDS and elderly acute myeloid leukemia, but there is little data focusing specifically on its efficacy in CMML. In this prospective, phase 2 Italian study, CMML patients received intravenous decitabine 20 mg/m2 per day on Days 1-5 of a 28-day treatment cycle. Response was evaluated after four and six cycles; patients responding at the end of six cycles could continue treatment with decitabine. Forty-three patients were enrolled; >50% were high-risk according to four CMML-specific scoring systems. In the intent-to-treat population (n=42), the overall response rate after six cycles was 47.6%, with seven complete responses (16.6%), eight marrow responses (19%), one partial response (2.4%) and four hematological improvements (9.5%). After a median follow-up of 51.5 months (range: 44.4-57.2), median overall survival was 17 months, with responders having a significantly longer survival than non-responders (P=0.02). Grade 3/4 anemia, neutropenia and thrombocytopenia occurred in 28.6%, 50% and 38% of patients, respectively. Decitabine appears to be an effective and well-tolerated treatment for patients with high-risk CMML.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. Valeria Santini received honorarium from Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson in Europe.
Figures



References
-
- Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Stein H, Vardiman JW (eds) World Health Organization Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC: Lyon, France, 2001.
-
- Swerdlow SH et al (eds) World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC: Lyon, France, 2016; in press.
-
- Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, Thiele J, Borowitz MJ, Le Beau MM et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood 2016; 127: 2391–2405. - PubMed
-
- Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, Jaffe ES, Pileri SA, Stein H et al (eds) World Health Organization Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. IARC: Lyon, France, 2008.
-
- Parikh S, Tefferi A. Chronic myelomonocytic leukemia: 2013 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 2013; 88: 968–974. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

