The metabolic function of cyclin D3-CDK6 kinase in cancer cell survival
- PMID: 28607489
- PMCID: PMC5516959
- DOI: 10.1038/nature22797
The metabolic function of cyclin D3-CDK6 kinase in cancer cell survival
Abstract
D-type cyclins (D1, D2 and D3) and their associated cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK4 and CDK6) are components of the core cell cycle machinery that drives cell proliferation. Inhibitors of CDK4 and CDK6 are currently being tested in clinical trials for patients with several cancer types, with promising results. Here, using human cancer cells and patient-derived xenografts in mice, we show that the cyclin D3-CDK6 kinase phosphorylates and inhibits the catalytic activity of two key enzymes in the glycolytic pathway, 6-phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase M2. This re-directs the glycolytic intermediates into the pentose phosphate (PPP) and serine pathways. Inhibition of cyclin D3-CDK6 in tumour cells reduces flow through the PPP and serine pathways, thereby depleting the antioxidants NADPH and glutathione. This, in turn, increases the levels of reactive oxygen species and causes apoptosis of tumour cells. The pro-survival function of cyclin D-associated kinase operates in tumours expressing high levels of cyclin D3-CDK6 complexes. We propose that measuring the levels of cyclin D3-CDK6 in human cancers might help to identify tumour subsets that undergo cell death and tumour regression upon inhibition of CDK4 and CDK6. Cyclin D3-CDK6, through its ability to link cell cycle and cell metabolism, represents a particularly powerful oncoprotein that affects cancer cells at several levels, and this property can be exploited for anti-cancer therapy.
Figures

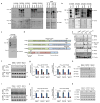


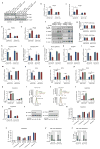

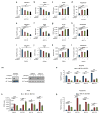



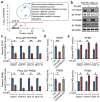
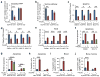

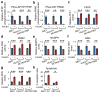
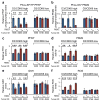
Comment in
-
Cell cycle: Division enzyme regulates metabolism.Nature. 2017 Jun 15;546(7658):357-358. doi: 10.1038/nature22504. Epub 2017 Jun 7. Nature. 2017. PMID: 28607481 No abstract available.
References
-
- Deshpande A, Sicinski P, Hinds PW. Cyclins and cdks in development and cancer: a perspective. Oncogene. 2005;24:2909–2915. - PubMed
-
- Dean JL, Thangavel C, McClendon AK, Reed CA, Knudsen ES. Therapeutic CDK4/6 inhibition in breast cancer: key mechanisms of response and failure. Oncogene. 2010;29:4018–4032. - PubMed
-
- Puyol M, et al. A synthetic lethal interaction between K-Ras oncogenes and Cdk4 unveils a therapeutic strategy for non-small cell lung carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 2010;18:63–73. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

