Altered Cytokine Expression and Barrier Properties after In Vitro Infection of Porcine Epithelial Cells with Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Probiotic Enterococcus faecium
- PMID: 28607532
- PMCID: PMC5457759
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/2748192
Altered Cytokine Expression and Barrier Properties after In Vitro Infection of Porcine Epithelial Cells with Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli and Probiotic Enterococcus faecium
Abstract
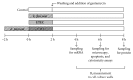
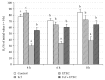
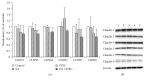
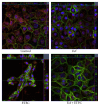
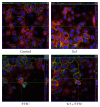
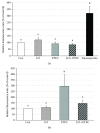
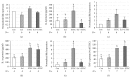
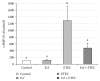
The aim of the present study was to elucidate the effects of the probiotic feed additive Enterococcus faecium NCIMB 10415 (E. faecium) on porcine jejunal epithelial cells (IPEC-J2) during an in vitro challenge with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC). Cells were incubated with E. faecium, ETEC, or both, and the effects on barrier function and structure and intra- and intercellular signaling were determined. Coincubation with E. faecium abolished the ETEC-induced decrease in transepithelial resistance (Rt) (p ≤ 0.05). No differences were seen in the expression levels of the intercellular connecting tight junction proteins examined. However, for the first time, a reorganization of the monolayer was observed in ETEC-infected cells but not in coincubated cells. ETEC induced an increase in cytotoxicity that was prevented by coincubation (p ≤ 0.05), whereas apoptosis rates were not affected by bacterial treatment. ETEC increased the mRNA expression and release of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1α, and IL-6 which could be prevented by coincubation for TNF-α mRNA expression and IL-6 protein (p ≤ 0.05). Likewise, cAMP concentrations elevated by ETEC were reduced in coincubated cells (p ≤ 0.05). These findings indicate a protective effect of the probiotic E. faecium on inflammatory responses during infection with ETEC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Enterococcus faecium NCIMB 10415 modulates epithelial integrity, heat shock protein, and proinflammatory cytokine response in intestinal cells.Mediators Inflamm. 2015;2015:304149. doi: 10.1155/2015/304149. Epub 2015 Apr 8. Mediators Inflamm. 2015. PMID: 25948884 Free PMC article.
-
The Inflammatory Response to Enterotoxigenic E. coli and Probiotic E. faecium in a Coculture Model of Porcine Intestinal Epithelial and Dendritic Cells.Mediators Inflamm. 2018 Dec 20;2018:9368295. doi: 10.1155/2018/9368295. eCollection 2018. Mediators Inflamm. 2018. PMID: 30670931 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a pathogenic ETEC strain and a probiotic Enterococcus faecium strain on the inflammasome response in porcine dendritic cells.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2018 Sep;203:78-87. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2018.08.004. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2018. PMID: 30143242
-
Effects of Ex Vivo Infection with ETEC on Jejunal Barrier Properties and Cytokine Expression in Probiotic-Supplemented Pigs.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 Apr;62(4):922-933. doi: 10.1007/s10620-016-4413-x. Epub 2016 Dec 19. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 27995406
-
Protective effects of Lactobacillus plantarum on epithelial barrier disruption caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in intestinal porcine epithelial cells.Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2016 Apr;172:55-63. doi: 10.1016/j.vetimm.2016.03.005. Epub 2016 Mar 5. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2016. PMID: 27032504
Cited by
-
Development and application of a multi-step porcine in vitro system to evaluate feedstuffs and feed additives for their efficacy in nutrient digestion, digesta characteristics, and intestinal immune responses.Anim Nutr. 2024 Mar 4;17:265-282. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2024.01.006. eCollection 2024 Jun. Anim Nutr. 2024. PMID: 38800740 Free PMC article.
-
Pretreatment with probiotic Enterococcus faecium NCIMB 11181 ameliorates necrotic enteritis-induced intestinal barrier injury in broiler chickens.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 16;9(1):10256. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-46578-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31311959 Free PMC article.
-
Toll-like receptor 5-mediated IL-17C expression in intestinal epithelial cells enhances epithelial host defense against F4+ ETEC infection.Vet Res. 2019 Jun 20;50(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13567-019-0665-8. Vet Res. 2019. PMID: 31221216 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effects of Grape Seed Oligomeric Proanthocyanidins in IPEC-J2-Escherichia coli/Salmonella Typhimurium Co-Culture.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Jan 15;11(1):110. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11010110. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35052987 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus thermophilus alters the expression of genes associated with innate and adaptive immunity in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells.PLoS One. 2020 Feb 11;15(2):e0228531. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228531. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32045425 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

