Characterization of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Like Cells Derived From Human iPSCs via Neural Crest Development and Their Application for Osteochondral Repair
- PMID: 28607560
- PMCID: PMC5451770
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/1960965
Characterization of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Like Cells Derived From Human iPSCs via Neural Crest Development and Their Application for Osteochondral Repair
Abstract
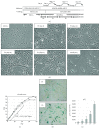
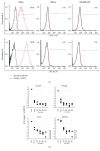
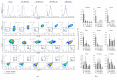
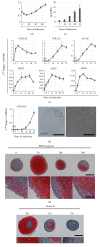
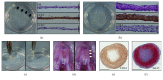
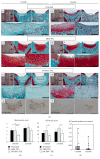
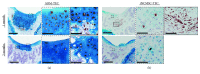
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are a promising cell source for the repair of skeletal disorders. Recently, neural crest cells (NCCs) were reported to be effective for inducing mesenchymal progenitors, which have potential to differentiate into osteochondral lineages. Our aim was to investigate the feasibility of MSC-like cells originated from iPSCs via NCCs for osteochondral repair. Initially, MSC-like cells derived from iPSC-NCCs (iNCCs) were generated and characterized in vitro. These iNCC-derived MSC-like cells (iNCMSCs) exhibited a homogenous population and potential for osteochondral differentiation. No upregulation of pluripotent markers was detected during culture. Second, we implanted iNCMSC-derived tissue-engineered constructs into rat osteochondral defects without any preinduction for specific differentiation lineages. The implanted cells remained alive at the implanted site, whereas they failed to repair the defects, with only scarce development of osteochondral tissue in vivo. With regard to tumorigenesis, the implanted cells gradually disappeared and no malignant cells were detected throughout the 2-month follow-up. While this study did not show that iNCMSCs have efficacy for repair of osteochondral defects when implanted under undifferentiated conditions, iNCMSCs exhibited good chondrogenic potential in vitro under appropriate conditions. With further optimization, iNCMSCs may be a new source for tissue engineering of cartilage.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Crest Cells for Tissue Regeneration and Disease Modeling.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Feb 22;12:39. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00039. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30853889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural crest-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells enhance cranial allograft integration.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021 May;10(5):797-809. doi: 10.1002/sctm.20-0364. Epub 2021 Jan 29. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33512772 Free PMC article.
-
Repair of Osteochondral Defects With Predifferentiated Mesenchymal Stem Cells of Distinct Phenotypic Character Derived From a Nanotopographic Platform.Am J Sports Med. 2020 Jun;48(7):1735-1747. doi: 10.1177/0363546520907137. Epub 2020 Mar 19. Am J Sports Med. 2020. PMID: 32191492
-
Osteochondral repair using a scaffold-free tissue-engineered construct derived from synovial mesenchymal stem cells and a hydroxyapatite-based artificial bone.Tissue Eng Part A. 2014 Sep;20(17-18):2291-304. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2013.0414. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Tissue Eng Part A. 2014. PMID: 24655056
-
Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Neural Crest Cells in Craniofacial Skeletal Research.Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:2849879. doi: 10.1155/2016/2849879. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Stem Cells Int. 2016. PMID: 27006661 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Osteochondral organoids: current advances, applications, and upcoming challenges.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024 Jun 21;15(1):183. doi: 10.1186/s13287-024-03790-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38902814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neural Crest Cells for Tissue Regeneration and Disease Modeling.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Feb 22;12:39. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00039. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30853889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of dexamethasone concentration on cartilage tissue formation from human synovial derived stem cells in vitro.Cytotechnology. 2018 Apr;70(2):819-829. doi: 10.1007/s10616-018-0191-y. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Cytotechnology. 2018. PMID: 29352392 Free PMC article.
-
Generation of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells with Low Immunogenicity from Human PBMC-Derived β2 Microglobulin Knockout Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720965529. doi: 10.1177/0963689720965529. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 33172291 Free PMC article.
-
Lineage-specific differentiation of osteogenic progenitors from pluripotent stem cells reveals the FGF1-RUNX2 association in neural crest-derived osteoprogenitors.Stem Cells. 2020 Sep;38(9):1107-1123. doi: 10.1002/stem.3206. Epub 2020 Jun 9. Stem Cells. 2020. PMID: 32442326 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

