The Transcription Factor Nrf2 Protects Angiogenic Capacity of Endothelial Colony-Forming Cells in High-Oxygen Radical Stress Conditions
- PMID: 28607561
- PMCID: PMC5451769
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/4680612
The Transcription Factor Nrf2 Protects Angiogenic Capacity of Endothelial Colony-Forming Cells in High-Oxygen Radical Stress Conditions
Abstract
Background: Endothelial colony forming cells (ECFCs) have shown a promise in tissue engineering of vascular constructs, where they act as endothelial progenitor cells. After implantation, ECFCs are likely to be subjected to elevated reactive oxygen species (ROS). The transcription factor Nrf2 regulates the expression of antioxidant enzymes in response to ROS.
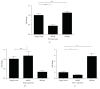
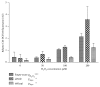
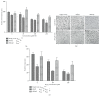
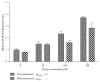
Methods: Stable knockdown of Nrf2 and Keap1 was achieved by transduction with lentiviral shRNAs; activation of Nrf2 was induced by incubation with sulforaphane (SFN). Expression of Nrf2 target genes was assessed by qPCR, oxidative stress was assessed using CM-DCFDA, and angiogenesis was quantified by scratch-wound and tubule-formation assays Results. Nrf2 knockdown led to a reduction of antioxidant gene expression and increased ROS. Angiogenesis was disturbed after Nrf2 knockdown even in the absence of ROS. Conversely, angiogenesis was preserved in high ROS conditions after knockdown of Keap1. Preincubation of ECFCs with SFN reduced intracellular ROS in the presence of H2O2 and preserved scratch-wound closure and tubule-formation.
Results: Nrf2 knockdown led to a reduction of antioxidant gene expression and increased ROS. Angiogenesis was disturbed after Nrf2 knockdown even in the absence of ROS. Conversely, angiogenesis was preserved in high ROS conditions after knockdown of Keap1. Preincubation of ECFCs with SFN reduced intracellular ROS in the presence of H2O2 and preserved scratch-wound closure and tubule-formation.
Conclusion: The results of this study indicate that Nrf2 plays an important role in the angiogenic capacity of ECFCs, particularly under conditions of increased oxidative stress. Pretreatment of ECFCs with SFN prior to implantation may be a protective strategy for tissue-engineered constructs or cell therapies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Protective Effect of Sulforaphane against Oxidative Stress through Activation of NRF2/ARE Pathway in Human Granulosa Cells.Cell J. 2021 Nov;23(6):692-700. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2021.7393. Epub 2021 Nov 23. Cell J. 2021. PMID: 34939763 Free PMC article.
-
Nrf2 deficiency induces oxidative stress and promotes RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:789-799. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.08.005. Epub 2013 Aug 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23954472
-
Protective roles of NRF2 signaling pathway in cobalt chloride-induced hypoxic cytotoxicity in human HaCaT keratinocytes.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018 Sep 15;355:189-197. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2018.06.030. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29966676
-
The Integrative Role of Sulforaphane in Preventing Inflammation, Oxidative Stress and Fatigue: A Review of a Potential Protective Phytochemical.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Jun 13;9(6):521. doi: 10.3390/antiox9060521. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress and Cancer: The Role of Nrf2.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018;18(6):538-557. doi: 10.2174/1568009617666171002144228. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 28969555 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro/Ex Vivo Models for the Study of Ischemia Reperfusion Injury during Kidney Perfusion.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 31;21(21):8156. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218156. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33142791 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Endothelial Colony-Forming Cells in Ischemic Disease: Strategies to Improve their Regenerative Efficacy.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 7;21(19):7406. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197406. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33036489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sesn2 attenuates the damage of endothelial progenitor cells induced by angiotensin II through regulating the Keap1/Nrf2 signal pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Nov 24;12(24):25505-25527. doi: 10.18632/aging.104156. Epub 2020 Nov 24. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33231566 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the redox system for cardiovascular regeneration in aging.Aging Cell. 2023 Dec;22(12):e14020. doi: 10.1111/acel.14020. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Aging Cell. 2023. PMID: 37957823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox Signaling and Its Impact on Skeletal and Vascular Responses to Spaceflight.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Oct 16;18(10):2153. doi: 10.3390/ijms18102153. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29035346 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

