Subclinical left ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients with metabolic syndrome: A case-control study using two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography
- PMID: 28607564
- PMCID: PMC5455323
Subclinical left ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients with metabolic syndrome: A case-control study using two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography
Abstract
Background: The dramatic increase in the prevalence of metabolic syndrome is associated with more increased cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in this group. Some recent studies suggested that metabolic syndrome is associated with increased risk of subclinical left ventricular (LV) systolic dysfunction. In the present cross-sectional case-control study, the utility of two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography (STE) was examined to detect early LV systolic dysfunction in this population.
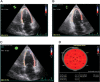
Methods: A total of 75 clinically asymptomatic subjects with left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) ≥ 55%, 39 without metabolic syndrome and 36 with metabolic syndrome, matched for gender and age, were enrolled in this case-control study. Metabolic syndrome was diagnosed using the National Cholesterol Education Program/Adult Treatment Panel III criteria. LV systolic function was assessed by STE-derived global and segmental longitudinal strain (εLL).
Results: Global εLL was significantly lower in patients with metabolic syndrome compared with normal population (-18.41 ± 2.20% vs. -21.2 ± 2.1%, P < 0.001). Segmental εLL was significantly lower in patients with metabolic syndrome in comparison to control group except for basal anteroseptal (-19.95 ± 2.90% vs. -21.15 ± 3.30%, P = 0.106), basal anterolateral (-17.5 ± 5.0% vs. -18.3 ± 4.1%, P = 0.437), and basal inferolateral segments (-18.1 ± 6.3% vs. -18.9 ± 4.1%, P = 0.526).
Conclusion: STE-derived longitudinal LV strain (εLL), a marker of subclinical cardiovascular disease, is impaired in asymptomatic individuals with metabolic syndrome and normal LVEF.
Keywords: Asymptomatic Disease; Metabolic Syndrome; Systole; Two-dimensional Echocardiography; Ventricular Dysfunction.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolic syndrome, strain, and reduced myocardial function: multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2014 Apr;102(4):327-35. doi: 10.5935/abc.20140040. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24844874 Free PMC article.
-
Use of Speckle Tracking Echocardiography to Assess Left Ventricular Systolic Function in Patients with Surgically Repaired Tetralogy of Fallot: Global and Segmental Assessment.Pediatr Cardiol. 2018 Dec;39(8):1669-1675. doi: 10.1007/s00246-018-1950-4. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Pediatr Cardiol. 2018. PMID: 30105466
-
Evaluation of subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in diabetic patients: longitudinal strain velocities and left ventricular dyssynchrony by two-dimensional speckle tracking echocardiography study.Echocardiography. 2014 Apr;31(4):456-63. doi: 10.1111/echo.12389. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Echocardiography. 2014. PMID: 24134395
-
Initial application of three-dimensional speckle-tracking echocardiography to detect subclinical left ventricular dysfunction and stratify cardiomyopathy associated with Duchenne muscular dystrophy in children.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Jan;35(1):67-76. doi: 10.1007/s10554-018-1436-8. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30105418
-
Incremental Value of Two Dimensional Speckle Tracking Echocardiography in the Functional Assessment and Characterization of Subclinical Left Ventricular Dysfunction.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2017;13(1):32-40. doi: 10.2174/1573403x12666160712095938. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2017. PMID: 27411342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of functional and structural echocardiography parameters in patients with frequent premature ventricular contractions without structural heart disease.ARYA Atheroscler. 2022 Mar;18(2):1-7. doi: 10.48305/arya.2022.16310. ARYA Atheroscler. 2022. PMID: 36819835 Free PMC article.
-
Early Left Ventricular Systolic Dysfunction Detected by Two-Dimensional Speckle-Tracking Echocardiography in Young Patients with Congenital Generalized Lipodystrophy.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Jan 13;13:107-115. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S233667. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 32021357 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic imaging in the management of patients with metabolic syndrome.Transl Res. 2018 Apr;194:1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2017.10.009. Epub 2017 Nov 22. Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29175480 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of speckle tracking in the evaluation of late subclinical myocardial damage in survivors of childhood acute leukaemia.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Sep;34(9):1373-1381. doi: 10.1007/s10554-018-1346-9. Epub 2018 Apr 2. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29611048
References
-
- Eckel RH, Kahn R, Robertson RM, Rizza RA. Preventing cardiovascular disease and diabetes: a call to action from the American Diabetes Association and the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2006;113(25):2943–6. - PubMed
-
- Levesque J, Lamarche B. The metabolic syndrome: definitions, prevalence and management. J Nutrigenet Nutrigenomics. 2008;1(3):100–8. - PubMed
-
- Nesbitt GC, Mankad S, Oh JK. Strain imaging in echocardiography: methods and clinical applications. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2009;25(Suppl 1):9–22. - PubMed
-
- Imbalzano E, Zito C, Carerj S, Oreto G, Mandraffino G, Cusma-Piccione M, et al. Left ventricular function in hypertension: new insight by speckle tracking echocardiography. Echocardiography. 2011;28(6):649–57. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials