Six-Food Elimination Diet and Topical Steroids are Effective for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Meta-Regression
- PMID: 28608048
- PMCID: PMC5709168
- DOI: 10.1007/s10620-017-4642-7
Six-Food Elimination Diet and Topical Steroids are Effective for Eosinophilic Esophagitis: A Meta-Regression
Abstract
Background: Topical corticosteroids or six-food elimination diet is recommended as initial therapy for eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Aims: We aimed to summarize published manuscripts that report outcomes of these therapies for EoE.
Methods: We performed a systematic review in MEDLINE, Web of Science, and Embase of published manuscripts describing topical fluticasone, topical budesonide, and six-food elimination diet as therapies for EoE. We conducted meta-analysis of symptom improvement and the change in peak mucosal eosinophil count, with heterogeneity between studies examined with meta-regression analysis.
Results: Systematic review yielded 51 articles that met inclusion criteria. Summary histologic response rates were 68.3% [95% prediction limits (PL) 16.2-96.0%] for fluticasone, 76.8% (95% PL 36.1-95.1%) for budesonide, and 69.0% (95% PL 31.9-91.4%) for six-food elimination diet. Corresponding decreases in eosinophil counts were 37.8 (95% PL 19.0-56.7), 62.5 (95% PL 125.6 to -0.67, and 44.6 (95% PL 26.5-62.7), respectively. Symptom response rates were 82.3% (95% PL 68.1-91.1%), 87.9% (95% PL 42.7-98.6%), and 87.3% (95% PL 64.5-96.3%), respectively. Meta-regression analyses decreased the initially large estimate of residual heterogeneity and suggested differences in histologic response rate associated with study populations' baseline eosinophil count and age.
Conclusions: The literature describing topical corticosteroids and six-food elimination diet consists of small studies with diverse methods and population characteristics. Meta-analysis with meta-regression shows initial histologic and symptomatic response rates on the same order of magnitude for topical corticosteroids and six-food elimination diet, but heterogeneity of study designs prevents direct comparison of modalities.
Keywords: Corticosteroids; Dietary elimination therapy; Eosinophilic esophagitis; Meta-analysis; Outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
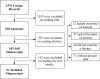









References
-
- Dellon ES, Gonsalves N, Hirano I, Furuta GT, et al. ACG clinical guideline: Evidenced based approach to the diagnosis and management of esophageal eosinophilia and eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108:679–692. quiz 693. - PubMed
-
- Liacouras CA, Furuta GT, Hirano I, Atkins D, et al. Eosinophilic esophagitis: updated consensus recommendations for children and adults. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011;128:3–20. e26. quiz 21–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

