Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food
- PMID: 28608841
- PMCID: PMC5486318
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph14060632
Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food
Abstract
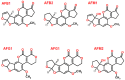
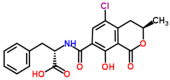
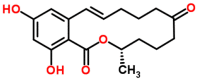
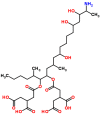
Mycotoxins are toxic secondary metabolites produced by certain filamentous fungi (molds). These low molecular weight compounds (usually less than 1000 Daltons) are naturally occurring and practically unavoidable. They can enter our food chain either directly from plant-based food components contaminated with mycotoxins or by indirect contamination from the growth of toxigenic fungi on food. Mycotoxins can accumulate in maturing corn, cereals, soybeans, sorghum, peanuts, and other food and feed crops in the field and in grain during transportation. Consumption of mycotoxin-contaminated food or feed can cause acute or chronic toxicity in human and animals. In addition to concerns over adverse effects from direct consumption of mycotoxin-contaminated foods and feeds, there is also public health concern over the potential ingestion of animal-derived food products, such as meat, milk, or eggs, containing residues or metabolites of mycotoxins. Members of three fungal genera, Aspergillus, Fusarium, and Penicillium, are the major mycotoxin producers. While over 300 mycotoxins have been identified, six (aflatoxins, trichothecenes, zearalenone, fumonisins, ochratoxins, and patulin) are regularly found in food, posing unpredictable and ongoing food safety problems worldwide. This review summarizes the toxicity of the six mycotoxins, foods commonly contaminated by one or more of them, and the current methods for detection and analysis of these mycotoxins.
Keywords: aflatoxin; analysis; chromatography; fungi; mycotoxins; rapid strip test; toxicology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
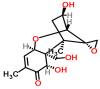
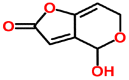
References
-
- Tanaka T., Hasegawa A., Yamamoto S., Lee U.S., Sugiura Y., Ueno Y. Worldwide contamination of cereals by Fusarium mycotoxins nivalenol, deoxynivalenol and zearalenone. I. Survey of 19 countries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988;36:979–983. doi: 10.1021/jf00083a019. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

