Polydatin alleviated radiation-induced lung injury through activation of Sirt3 and inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
- PMID: 28609013
- PMCID: PMC5706589
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13230
Polydatin alleviated radiation-induced lung injury through activation of Sirt3 and inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition
Abstract
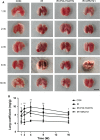
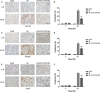
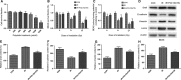
Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI) is one of the most common and fatal complications of thoracic radiotherapy. It is characterized with two main features including early radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis in later phase. This study was to investigate the potential radioprotective effects of polydatin (PD), which was shown to exert anti-inflammation and anti-oxidative capacities in other diseases. In this study, we demonstrated that PD-mitigated acute inflammation and late fibrosis caused by irradiation. PD treatment inhibited TGF-β1-Smad3 signalling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Moreover, radiation-induced imbalance of Th1/Th2 was also alleviated by PD treatment. Besides its free radical scavenging capacity, PD induced a huge increase of Sirt3 in culture cells and lung tissues. The level of Nrf2 and PGC1α in lung tissues was also elevated. In conclusion, our data showed that PD attenuated radiation-induced lung injury through inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition and increased the expression of Sirt3, suggesting PD as a novel potential radioprotector for RILI.
Keywords: epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT); free radicals; polydatin (PD); radiation-induced lung injury.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures


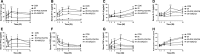



Similar articles
-
Polydatin attenuates reactive oxygen species-induced airway remodeling by promoting Nrf2-mediated antioxidant signaling in asthma mouse model.Life Sci. 2019 Feb 1;218:25-30. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.08.013. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 30092299
-
Glucosamine protects against radiation-induced lung injury via inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Sep;24(18):11018-11023. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15662. Epub 2020 Jul 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32700471 Free PMC article.
-
Ionizing Radiation Promotes Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Lung Epithelial Cells by TGF-β-producing M2 Macrophages.In Vivo. 2019 Nov-Dec;33(6):1773-1784. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11668. In Vivo. 2019. PMID: 31662502 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T Cells: An Emerging Player in Radiation-Induced Lung Injury.Front Immunol. 2020 Aug 4;11:1769. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01769. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32849634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radiation-Induced Pulmonary Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: A Review on Targeting Molecular Pathways and Mediators.Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19(10):1191-1204. doi: 10.2174/1389450119666180207092234. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 29412104 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological management of ionizing radiation injuries: current and prospective agents and targeted organ systems.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020 Feb;21(3):317-337. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2019.1702968. Epub 2020 Jan 11. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31928256 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polydatin attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting YAP expression and nuclear translocation.Front Physiol. 2022 Oct 7;13:927794. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.927794. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36277194 Free PMC article.
-
E-Stilbenes: General Chemical and Biological Aspects, Potential Pharmacological Activity Based on the Nrf2 Pathway.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 9;17(2):232. doi: 10.3390/ph17020232. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crossed Pathways for Radiation-Induced and Immunotherapy-Related Lung Injury.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 1;12:774807. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.774807. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34925345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis inhibitor alleviates Radiation-induced lung fibrosis (RILF) via down-regulation of TGF-β1.J Inflamm (Lond). 2019 May 29;16:11. doi: 10.1186/s12950-019-0216-0. eCollection 2019. J Inflamm (Lond). 2019. PMID: 31160885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vujaskovic Z, Marks LB, Anscher MS. The physical parameters and molecular events associated with radiation‐induced lung toxicity. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2000; 10: 296–307. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

