Purification of family B G protein-coupled receptors using nanodiscs: Application to human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
- PMID: 28609478
- PMCID: PMC5469476
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179568
Purification of family B G protein-coupled receptors using nanodiscs: Application to human glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
Abstract
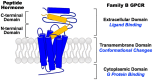
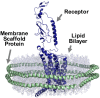
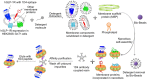
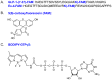
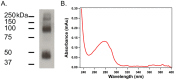
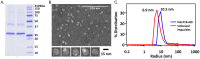
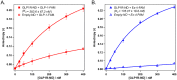
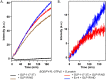
Family B G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) play vital roles in hormone-regulated homeostasis. They are drug targets for metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes and osteoporosis. Despite their importance, the signaling mechanisms for family B GPCRs at the molecular level remain largely unexplored due to the challenges in purification of functional receptors in sufficient amount for biophysical characterization. Here, we purified the family B GPCR human glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor (GLP1R), whose agonists, e.g. exendin-4, are used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The receptor was expressed in HEK293S GnTl- cells using our recently developed protocol. The protocol incorporates the receptor into the native-like lipid environment of reconstituted high density lipoprotein (rHDL) particles, also known as nanodiscs, immediately after the membrane solubilization step followed by chromatographic purification, minimizing detergent contact with the target receptor to reduce denaturation and prolonging stabilization of receptor in lipid bilayers without extra steps of reconstitution. This method yielded purified GLP1R in nanodiscs that could bind to GLP-1 and exendin-4 and activate Gs protein. This nanodisc purification method can potentially be a general strategy to routinely obtain purified family B GPCRs in the 10s of microgram amounts useful for spectroscopic analysis of receptor functions and activation mechanisms.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Is exenatide advancing the treatment of type 2 diabetes?Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2006 Jan;7(1):109-12. doi: 10.1517/14656566.7.1.109. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2006. PMID: 16370928 Review.
-
The value of short- and long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 agonists in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: experience with exenatide.Curr Med Res Opin. 2016;32(1):61-76. doi: 10.1185/03007995.2015.1103214. Epub 2015 Nov 11. Curr Med Res Opin. 2016. PMID: 26439329 Review.
-
Evaluation of Drug Efficacy of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and DPP-4 Inhibitors Based on Target Molecular Binding Occupancy.Biol Pharm Bull. 2018;41(2):153-157. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00237. Biol Pharm Bull. 2018. PMID: 29386477
-
Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists in Cardiac Disorders.Ann Pharmacother. 2016 Dec;50(12):1041-1050. doi: 10.1177/1060028016663218. Epub 2016 Aug 16. Ann Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27531946 Review.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues for Type 2 diabetes mellitus: current and emerging agents.Drugs. 2011 Sep 10;71(13):1675-88. doi: 10.2165/11592810-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2011. PMID: 21902291 Review.
Cited by
-
The Effect of Cell Surface Expression and Linker Sequence on the Recruitment of Arrestin to the GIP Receptor.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Aug 13;11:1271. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01271. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32903502 Free PMC article.
-
Purification of the full-length, membrane-associated form of the antiviral enzyme viperin utilizing nanodiscs.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 13;12(1):11909. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16233-z. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35831548 Free PMC article.
-
HDL and Therapy.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022;1377:171-187. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-1592-5_14. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2022. PMID: 35575930
-
A human antibody against human endothelin receptor type A that exhibits antitumor potency.Exp Mol Med. 2021 Sep;53(9):1437-1448. doi: 10.1038/s12276-021-00678-9. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Exp Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34588605 Free PMC article.
-
The Endocannabinoid System as a Target in Cancer Diseases: Are We There Yet?Front Pharmacol. 2019 Apr 5;10:339. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00339. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31024307 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fredriksson R, Lagerstrom MC, Lundin LG, Schioth HB. The G-protein-coupled receptors in the human genome form five main families. Phylogenetic analysis, paralogon groups, and fingerprints. Molecular pharmacology. 2003;63(6):1256–72. doi: 10.1124/mol.63.6.1256 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lagerstrom MC, Schioth HB. Structural diversity of G protein-coupled receptors and significance for drug discovery. Nature reviews Drug discovery. 2008;7(4):339–57. doi: 10.1038/nrd2518 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Liu Y, Cai Y, Liu W, Li XH, Rhoades E, Yan EC. Triblock peptide-linker-lipid molecular design improves potency of peptide ligands targeting family B G protein-coupled receptors. Chem Commun (Camb). 2015;51(28):6157–60. - PubMed
-
- Salon JA, Lodowski DT, Palczewski K. The significance of G protein-coupled receptor crystallography for drug discovery. Pharmacol Rev. 2011;63(4):901–37. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003350 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

