Familial 5q12.3 Microdeletion: Evidence for a Locus Associated with Epilepsy
- PMID: 28611550
- PMCID: PMC5465700
- DOI: 10.1159/000454725
Familial 5q12.3 Microdeletion: Evidence for a Locus Associated with Epilepsy
Abstract
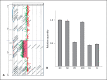
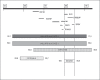
The clinical use of array comparative genomic hybridization (array CGH) has allowed the identification of very rare deletion and duplication disorders, such as 5q12 deletion syndrome (OMIM 615668) described as a contiguous gene deletion syndrome of chromosome 5q12. Chromosome microdeletions including band 5q12 have rarely been reported and have been associated with different phenotypes showing postnatal growth restriction, intellectual disability, epileptic seizures, hyperactivity, and ocular abnormalities. In this study, we describe a family in which array-CGH analysis revealed the presence of an interstitial microdeletion spanning approximately 2.9 Mb in the 5q12 region. The microdeletion is associated with epilepsy in the father and 2 siblings (a boy and a girl). So far, this is the first report in which a familial microdeletion 5q12 manifests in epilepsy. We suggest that this familial microdeletion could delineate a locus for susceptibility to epilepsy.
Keywords: Array CGH; Epilepsy; Interstitial microdeletion 5q.
Figures
References
-
- Borg JP, Marchetto S, Le Bivic A, Ollendorff V, Jaulin-Bastard F, et al. ERBIN: a basolateral PDZ protein that interacts with the mammalian ERBB2/HER2 receptor. Nat Cell Biol. 2000;2:407–414. - PubMed
-
- Cetin Z, Yakut S, Clark OA, Mihci E, Berker S, Luleci G. A 5q12.1–5q12.3 microdeletion in a case with a balanced exceptional complex chromosomal rearrangement. Gene. 2013;516:176–180. - PubMed
-
- Holder JL, Jr, Cheung SW. Refinement of the postnatal growth restriction locus of chromosome 5q12–13 deletion syndrome. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2015;167A:2737–2741. - PubMed
-
- Jaillard S, Andrieux J, Plessis G, Krepischi AC, Lucas J, et al. Deletion 5q12.1: delineation of a phenotype including mental retardation and ocular defects. Am J Med Genet. 2011;155A:725–731. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

