CD24 Expression Is Increased in 5-Fluorouracil-Treated Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Cells
- PMID: 28611669
- PMCID: PMC5447731
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00321
CD24 Expression Is Increased in 5-Fluorouracil-Treated Esophageal Adenocarcinoma Cells
Abstract
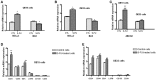
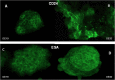
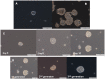
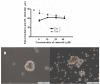
The cancer stem cell (CSC) model suggests that there are subsets of cells within a tumor with increased proliferation and self-renewal capacity, which play a key role in therapeutic resistance. The importance of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in carcinogenesis has been previously established and the use of COX-2 inhibitors as celecoxib has been shown to exert antitumor effects. The present study investigated whether treatment of esophageal adenocarcinoma (EAC) cells with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) or the growth of tumor spheres increased the proportion of CSCs and also if treatment with celecoxib was able to reduce the putative CSC markers in this tumor. OE19 and OE33 EAC cells surviving 5-FU exposure exhibited an increase in CSC markers CD24 and ABCG2 and also an increased resistance to apoptosis. EAC cell lines had the capacity to form multiple spheres displaying typical CSC functionalities such as self-renewal and increased CD24 levels. In addition, after the induction of differentiation, cancer cells reached levels of CD24 similar to those observed in the parental cells. Treatment with celecoxib alone or in combination with 5-FU also resulted in a reduction of CD24 expression. Moreover, celecoxib inhibited the growth of tumor spheres. These findings showing a reduction in CSC markers induced by celecoxib suggest that the COX-2 inhibitor might be a candidate for combined chemotherapy in the treatment of EAC. However, additional clinical and experimental studies are needed.
Keywords: 5-fluorouracil; CD24; cancer stem cells; celecoxib; esophageal adenocarcinoma.
Figures




References
-
- Abnet C. C., Freedman N. D., Kamangar F., Leitzmann M. F., Hollenbeck A. R., Schatzkin A. (2009). Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of gastric and oesophageal adenocarcinomas: results from a cohort study and a meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 100, 551–557. 10.1038/sj.bjc.6604880 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aigner S., Ramos C. L., Hafezi-Moghadam A., Lawrence M. B., Friederichs J., Altevogt P., et al. . (1998). CD24 mediates rolling of breast carcinoma cells on P-selectin. FASEB J. 12, 1241–1251. - PubMed
-
- Altorki N. K., Christos P., Port J. L., Lee P. C., Mirza F., Spinelli C., et al. . (2011). Preoperative taxane-based chemotherapy and celecoxib for carcinoma of the esophagus and gastroesophageal junction: results of a phase 2 trial. J. Thorac. Oncol. 6, 1121–1127. 10.1097/JTO.0b013e31821529a9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

