Utility of spherical human liver microtissues for prediction of clinical drug-induced liver injury
- PMID: 28612260
- PMCID: PMC5515971
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-017-2002-1
Utility of spherical human liver microtissues for prediction of clinical drug-induced liver injury
Abstract
Drug-induced liver injury (DILI) continues to be a major source of clinical attrition, precautionary warnings, and post-market withdrawal of drugs. Accordingly, there is a need for more predictive tools to assess hepatotoxicity risk in drug discovery. Three-dimensional (3D) spheroid hepatic cultures have emerged as promising tools to assess mechanisms of hepatotoxicity, as they demonstrate enhanced liver phenotype, metabolic activity, and stability in culture not attainable with conventional two-dimensional hepatic models. Increased sensitivity of these models to drug-induced cytotoxicity has been demonstrated with relatively small panels of hepatotoxicants. However, a comprehensive evaluation of these models is lacking. Here, the predictive value of 3D human liver microtissues (hLiMT) to identify known hepatotoxicants using a panel of 110 drugs with and without clinical DILI has been assessed in comparison to plated two-dimensional primary human hepatocytes (PHH). Compounds were treated long-term (14 days) in hLiMT and acutely (2 days) in PHH to assess drug-induced cytotoxicity over an 8-point concentration range to generate IC50 values. Regardless of comparing IC50 values or exposure-corrected margin of safety values, hLiMT demonstrated increased sensitivity in identifying known hepatotoxicants than PHH, while specificity was consistent across both assays. In addition, hLiMT out performed PHH in correctly classifying hepatotoxicants from different pharmacological classes of molecules. The hLiMT demonstrated sufficient capability to warrant exploratory liver injury biomarker investigation (miR-122, HMGB1, α-GST) in the cell-culture media. Taken together, this study represents the most comprehensive evaluation of 3D spheroid hepatic cultures up to now and supports their utility for hepatotoxicity risk assessment in drug discovery.
Keywords: DILI; Drug discovery; Hepatocyte; Hepatotoxicity; Microtissue; Spheroid culture.
Conflict of interest statement
M. K., S. S., J. M. K. and S. M. are employees of InSphero AG. All cytotoxicity studies in hLiMT were performed at InSphero AG under conditions where the identities of the 110 compounds were blinded to them.
Figures


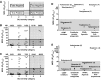

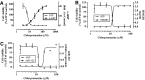
Comment in
-
Highlight report: prediction of drug induced liver injury (DILI) with human hepatocytes in vitro.Arch Toxicol. 2017 Dec;91(12):4021-4022. doi: 10.1007/s00204-017-2132-5. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 29181616 No abstract available.
-
Future perspectives of DILI prediction in vitro.Arch Toxicol. 2019 Sep;93(9):2705-2706. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02530-6. Epub 2019 Jul 31. Arch Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 31367904 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

