Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Paclitaxel Monotherapy: An Updated Literature Review
- PMID: 28612269
- PMCID: PMC8572663
- DOI: 10.1007/s40262-017-0563-z
Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Paclitaxel Monotherapy: An Updated Literature Review
Abstract
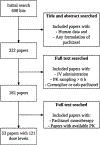
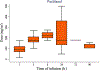
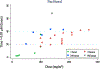
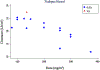
Paclitaxel is an anticancer agent efficacious in the treatment of ovarian, breast, and lung cancer. Due to a strong link between the pharmacokinetics and therapeutic efficacy of paclitaxel, we reviewed the literature on paclitaxel pharmacokinetics. Systematic data mining was performed to extract the maximum concentration (C max), clearance (CL), and time of paclitaxel plasma concentration above 0.05 µmol/L (T > 0.05 µmol/L) following monotherapy of both the widely used cremophor-diluted paclitaxel and nanoparticle albumin-bound (nab-)paclitaxel. We identified a total of 53 studies yielding 121 aggregated pharmacokinetic profiles for paclitaxel monotherapy and extracted reported mean and median estimates of pharmacokinetic parameters. Paclitaxel has been studied formally at doses of 15-825 mg/m2 and infused over 0.5-96 h; included studies examined both weekly and every 3-weeks dosing cycles. The most widely used dose of cremophor-diluted paclitaxel, 175 mg/m2 given as a 3-h infusion, leads to an interstudy median C max of 5.1 µmol/L [interquartile range (IQR) 4.5-5.7], CL of 12.0 L/h/m2 (IQR 10.9-12.9), and T > 0.05 µmol/L of 23.8 h (IQR 21.5-26.8). Importantly, the significant interindividual variation widely reported in the literature is not reflected in these interstudy estimates of pharmacokinetic parameters. Cremophor-diluted paclitaxel pharmacokinetics are non-linear following short (<6 h) but not long (>24 h) infusions. A similar pattern of non-linearity was observed for nab-paclitaxel, although the number of studies was limited. The pharmacokinetics of paclitaxel monotherapy have been widely studied at numerous dose levels of the Cremophor EL® formulation, but are less well-characterized for the newer nab-paclitaxel formulation. In conclusion, paclitaxel pharmacokinetics are non-linear for short infusion times but not for longer infusions. Whether a similar conclusion can be drawn for nab-paclitaxel formulations requires further study.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: No authors have conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Bishop JF, Dewar J, Toner GC, Smith J, Tattersall MH, Olver IN, et al. Initial paclitaxel improves outcome compared with CMFP combination chemotherapy as front-line therapy in untreated metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol 1999;17:2355–64. - PubMed
-
- Ozols RF, Bundy BN, Greer BE, Fowler JM, Clarke-Pearson D, Burger RA, et al. Phase III trial of carboplatin and paclitaxel compared with cisplatin and paclitaxel in patients with optimally resected stage III ovarian cancer: a Gynecologic Oncology Group study. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol 2003;21:3194–200. - PubMed
-
- Socinski MA. Cytotoxic chemotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a review of standard treatment paradigms. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res 2004;10:4210s–4214s. - PubMed
-
- Mathew AE, Mejillano MR, Nath JP, Himes RH, Stella VJ. Synthesis and evaluation of some water-soluble prodrugs and derivatives of taxol with antitumor activity. J. Med. Chem 1992;35:145–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

