Model-based optimization approaches for precision medicine: A case study in presynaptic dopamine overactivity
- PMID: 28614410
- PMCID: PMC5470743
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179575
Model-based optimization approaches for precision medicine: A case study in presynaptic dopamine overactivity
Abstract
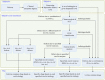
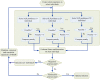
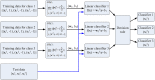
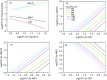
Precision medicine considers an individual's unique physiological characteristics as strongly influential in disease vulnerability and in response to specific therapies. Predicting an individual's susceptibility to developing an illness, making an accurate diagnosis, maximizing therapeutic effects, and minimizing adverse effects for treatment are essential in precision medicine. We introduced model-based precision medicine optimization approaches, including pathogenesis, biomarker detection, and drug target discovery, for treating presynaptic dopamine overactivity. Three classes of one-hit and two-hit enzyme defects were detected as the causes of disease states by the optimization approach of pathogenesis. The cluster analysis and support vector machine was used to detect optimal biomarkers in order to discriminate the accurate etiology from three classes of disease states. Finally, the fuzzy decision-making method was employed to discover common and specific drug targets for each classified disease state. We observed that more accurate diagnoses achieved higher satisfaction grades and dosed fewer enzyme targets to treat the disease. Furthermore, satisfaction grades for common drugs were lower than for specific ones, but common drugs could simultaneously treat several disease states that had different etiologies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fuzzy Decision Making Approach to Identify Optimum Enzyme Targets and Drug Dosage for Remedying Presynaptic Dopamine Deficiency.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 13;11(10):e0164589. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164589. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27736960 Free PMC article.
-
Precision cancer medicine: where to target?Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Oct;36(10):1161-2. doi: 10.1038/aps.2015.93. Epub 2015 Sep 21. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 26388154 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Leveraging big data to transform target selection and drug discovery.Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016 Mar;99(3):285-97. doi: 10.1002/cpt.318. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26659699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical proteomics-driven precision medicine for targeted cancer therapy: current overview and future perspectives.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2016;13(4):367-81. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2016.1159959. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2016. PMID: 26923776 Review.
-
Automated Detection of Cancer Associated Genes Using a Combined Fuzzy-Rough-Set-Based F-Information and Water Swirl Algorithm of Human Gene Expression Data.PLoS One. 2016 Dec 9;11(12):e0167504. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167504. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27936033 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Artificial intelligence and machine learning-aided drug discovery in central nervous system diseases: State-of-the-arts and future directions.Med Res Rev. 2021 May;41(3):1427-1473. doi: 10.1002/med.21764. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Med Res Rev. 2021. PMID: 33295676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revolution in Health Care: How Will Data Science Impact Doctor-Patient Relationships?Front Public Health. 2018 Apr 3;6:99. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2018.00099. eCollection 2018. Front Public Health. 2018. PMID: 29666789 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Artificial intelligence and machine-learning approaches in structure and ligand-based discovery of drugs affecting central nervous system.Mol Divers. 2023 Apr;27(2):959-985. doi: 10.1007/s11030-022-10489-3. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Mol Divers. 2023. PMID: 35819579 Review.
References
-
- Collins FS, Varmus H. A new initiative on precision medicine. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(9):793–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1500523. . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jameson JL, Longo DL. Precision medicine—personalized, problematic, and promising. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(23):2229–34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMsb1503104. . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mehta R, Jain RK, Badve S. Personalized medicine: the road ahead. Clin Breast Cancer. 2011;11(1):20–6. doi: 10.3816/CBC.2011.n.004. . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ozomaro U, Wahlestedt C, Nemeroff CB. Personalized medicine in psychiatry: problems and promises. BMC Med. 2013;11:132 doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-132. ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPMC3668172. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tandon R, Keshavan MS, Nasrallah HA. Schizophrenia,“just the facts” what we know in 2008. 2. Epidemiology and etiology. Schizophrenia research. 2008;102(1):1–18. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

