General Strategy for Direct Cytosolic Protein Delivery via Protein-Nanoparticle Co-engineering
- PMID: 28614657
- PMCID: PMC5766003
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.7b02884
General Strategy for Direct Cytosolic Protein Delivery via Protein-Nanoparticle Co-engineering
Abstract
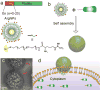
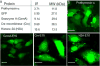
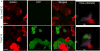
Endosomal entrapment is a key hurdle for most intracellular protein-based therapeutic strategies. We report a general strategy for efficient delivery of proteins to the cytosol through co-engineering of proteins and nanoparticle vehicles. The proteins feature an oligo(glutamate) sequence (E-tag) that binds arginine-functionalized gold nanoparticles, generating hierarchical spherical nanoassemblies. These assemblies fuse with cell membranes, releasing the E-tagged protein directly into the cytosol. Five different proteins with diverse charges, sizes, and functions were effectively delivered into cells, demonstrating the generality of our method. Significantly, the engineered proteins retained activity after cytosolic delivery, as demonstrated through the delivery of active Cre recombinase, and granzyme A to kill cancer cells.
Keywords: cytosolic protein delivery; hierarchical nanoassembly; membrane fusion; nanoparticles; protein engineering.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): V.M.R and R.M. submitted a non-provisional patent to USPTO (Application number PCT/US2016/015711) on the invention.
Figures



References
-
- Gu Z, Biswas A, Zhao M, Tang Y. Tailoring Nanocarriers for Intracellular Protein Delivery. Chem Soc Rev. 2011;40:3638–3655. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

