Cytoplasmic Dynein Transports Axonal Microtubules in a Polarity-Sorting Manner
- PMID: 28614709
- PMCID: PMC5523108
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.05.064
Cytoplasmic Dynein Transports Axonal Microtubules in a Polarity-Sorting Manner
Abstract
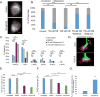
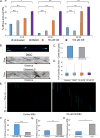
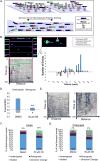
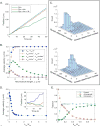
Axonal microtubules are predominantly organized into a plus-end-out pattern. Here, we tested both experimentally and with computational modeling whether a motor-based polarity-sorting mechanism can explain this microtubule pattern. The posited mechanism centers on cytoplasmic dynein transporting plus-end-out and minus-end-out microtubules into and out of the axon, respectively. When cytoplasmic dynein was acutely inhibited, the bi-directional transport of microtubules in the axon was disrupted in both directions, after which minus-end-out microtubules accumulated in the axon over time. Computational modeling revealed that dynein-mediated transport of microtubules can establish and preserve a predominantly plus-end-out microtubule pattern as per the details of the experimental findings, but only if a kinesin motor and a static cross-linker protein are also at play. Consistent with the predictions of the model, partial depletion of TRIM46, a protein that cross-links axonal microtubules in a manner that influences their polarity orientation, leads to an increase in microtubule transport.
Keywords: TRIM46; axon; cytoplasmic dynein; microtubule; microtubule polarity orientation; microtubule sliding; microtubule transport; neuron.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- AHMAD FJ, HE Y, MYERS KA, HASAKA TP, FRANCIS F, BLACK MM, BAAS PW. Effects of dynactin disruption and dynein depletion on axonal microtubules. Traffic. 2006;7:524–37. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

