Dissecting the human microbiome with single-cell genomics
- PMID: 28615076
- PMCID: PMC5471897
- DOI: 10.1186/s13073-017-0448-7
Dissecting the human microbiome with single-cell genomics
Abstract
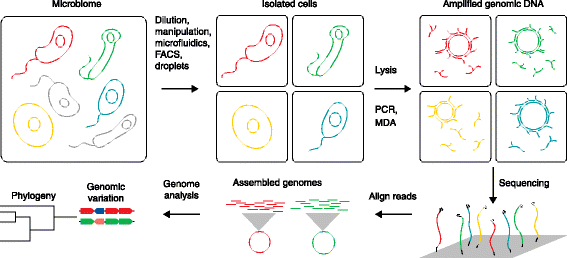
Recent advances in genome sequencing of single microbial cells enable the assignment of functional roles to members of the human microbiome that cannot currently be cultured. This approach can reveal the genomic basis of phenotypic variation between closely related strains and can be applied to the targeted study of immunogenic bacteria in disease.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

