Impaired Downregulation of NKG2D Ligands by Nef Proteins from Elite Controllers Sensitizes HIV-1-Infected Cells to Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity
- PMID: 28615199
- PMCID: PMC5533916
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00109-17
Impaired Downregulation of NKG2D Ligands by Nef Proteins from Elite Controllers Sensitizes HIV-1-Infected Cells to Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity
Abstract
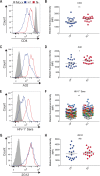
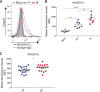
HIV-1 Nef clones isolated from a rare subset of HIV-1-infected elite controllers (EC), with the ability to suppress viral load to undetectable levels in the absence of antiretroviral therapy, are unable to fully downregulate CD4 from the plasma membrane of CD4+ T cells. Residual CD4 left at the plasma membrane allows Env-CD4 interaction, which leads to increased exposure of Env CD4-induced epitopes and increases susceptibility of infected cells to antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). ADCC is mediated largely by natural killer (NK) cells, which control their activation status through the cumulative signals received through activating and inhibitory receptors. Recently, the activating NKG2D receptor was demonstrated to positively influence ADCC responses. Since HIV-1 Nef has been reported to reduce the expression of NKG2D ligands, we evaluated the relative abilities of Nef from EC and progressors to downmodulate NKG2D ligands. Furthermore, we assessed the impact of EC and progressor Nef on the ADCC susceptibility of HIV-1-infected cells. We observed a significantly increased expression of NKG2D ligands on cells infected with viruses coding for Nef from EC. Importantly, NKG2D ligand expression levels correlated with enhanced susceptibility of HIV-1-infected cells to ADCC. The biological significance of this correlation was corroborated by the demonstration that antibody-mediated blockade of NKG2D significantly reduced ADCC of cells infected with viruses carrying Nef from EC. These results suggest the involvement of NKG2D-NKG2D ligand interactions in the enhanced susceptibility of EC HIV-1-infected cells to ADCC responses.IMPORTANCE Attenuated Nef functions have been reported in HIV-1 isolated from EC. The inability of elite controller Nef to fully remove CD4 from the surface of infected cells enhanced their susceptibility to elimination by ADCC. We now show that downregulation of NKG2D ligands by HIV-1 Nef from EC is inefficient and leaves infected cells susceptible to ADCC. These data suggest a critical role for NKG2D ligands in anti-HIV-1 ADCC responses.
Keywords: ADCC; CD4; HIV-1; NKG2D; Nef; elite controllers; gp120.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures



References
-
- Deacon NJ, Tsykin A, Solomon A, Smith K, Ludford-Menting M, Hooker DJ, McPhee DA, Greenway AL, Ellett A, Chatfield C, Lawson VA, Crowe S, Maerz A, Sonza S, Learmont J, Sullivan JS, Cunningham A, Dwyer D, Dowton D, Mills J. 1995. Genomic structure of an attenuated quasi species of HIV-1 from a blood transfusion donor and recipients. Science 270:988–991. doi:10.1126/science.270.5238.988. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zaunders JJ, Geczy AF, Dyer WB, McIntyre LB, Cooley MA, Ashton LJ, Raynes-Greenow CH, Learmont J, Cooper DA, Sullivan JS. 1999. Effect of long-term infection with nef-defective attenuated HIV type 1 on CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes: increased CD45RO+CD4+ T lymphocytes and limited activation of CD8+ T lymphocytes. AIDS Res Hum Retrovir 15:1519–1527. doi:10.1089/088922299309801. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

