Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and their transcriptional control of inflammatory responses
- PMID: 28615453
- PMCID: PMC5535013
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.R116.760884
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and their transcriptional control of inflammatory responses
Abstract
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have emerged as potential key regulators of the inflammatory response, particularly by modulating the transcriptional control of inflammatory genes. lncRNAs may act as an enhancer or suppressor to inflammatory transcription, function as scaffold molecules through interactions with RNA-binding proteins in chromatin remodeling complexes, and modulate dynamic and epigenetic control of inflammatory transcription in a gene-specific and time-dependent fashion. Here, we will review recent literature regarding the role of lncRNAs in transcriptional control of inflammatory responses. Better understanding of lncRNA regulation of inflammation will provide novel targets for the development of new therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: NF-κB; chromatin remodeling; epigenetics; inflammation; long noncoding RNA (long ncRNA, lncRNA); toll-like receptor (TLR); transcription regulation.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
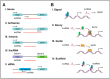
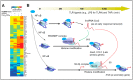

References
-
- Pawate S., Shen Q., Fan F., and Bhat N. R. (2004) Redox regulation of glial inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide and interferon γ. J. Neurosci. Res. 77, 540–551 - PubMed
-
- Jung Y. J., Isaacs J. S., Lee S., Trepel J., and Neckers L. (2003) IL-1β-mediated up-regulation of HIF-1α via an NFκB/COX-2 pathway identifies HIF-1 as a critical link between inflammation and oncogenesis. FASEB J. 17, 2115–2117 - PubMed
-
- Adhikari A., Xu M., and Chen Z. J. (2007) Ubiquitin-mediated activation of TAK1 and IKK. Oncogene 26, 3214–3226 - PubMed
-
- Fitzgerald D. C., Meade K. G., McEvoy A. N., Lillis L., Murphy E. P., MacHugh D. E., and Baird A. W. (2007) Tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) increases nuclear factor κB (NFκB) activity in and interleukin-8 (IL-8) release from bovine mammary epithelial cells. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 116, 59–68 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

