Warfarin-related nephropathy induced by three different vitamin K antagonists: analysis of 13 biopsy-proven cases
- PMID: 28616216
- PMCID: PMC5466118
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfw133
Warfarin-related nephropathy induced by three different vitamin K antagonists: analysis of 13 biopsy-proven cases
Abstract
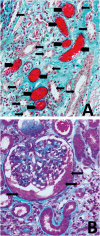
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) with renal tubular obstruction by red blood cell casts (RBCC) has been described in patients treated with warfarin and is known as warfarin-related nephropathy (WRN). Methods: To determine whether other vitamin K antagonists (VKA) cause WRN, we retrospectively collected and analyzed the clinical and histological data of 13 patients treated with different VKA (seven with fluindione, four with warfarin and two with acenocoumarol) in seven French hospitals. Results: They all developed gross hematuria following overanticoagulation complicated by severe AKI (median serum creatinine concentration = 693 μmol/L). Histological analysis of the kidney biopsies highlighted the presence of intratubular RBCC and acute tubular necrosis in all patients and of an underlying kidney disease in 12 patients. WRN was suspected in patients treated with warfarin; however, the initial diagnosis was incorrect in six of the nine patients treated with other VKA. Nine patients progressed to chronic kidney disease, one fully recovered renal function, two died and one still needs dialysis. Conclusions: This is the first report of AKI caused by fluindione. In agreement with the recent publication on AKI in two patients treated with dabigatran, we suggest that the term 'anticoagulant-related nephropathy' is more appropriate than WRN. Gross hematuria in patients with an underlying kidney disease and treated with VKA requires rapid control of the international normalized ratio and renal function monitoring.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; drug nephrotoxicity; renal biopsy; vitamin k antagonists; warfarin-related nephropathy.
Figures

References
-
- Rapport sur les anticoagulants en France en 2014: Etat des lieux, synthèse et surveillance. http://ansm.sante.fr/content/download/61981/795269/version/2/file/ANSM-r... (22 April 2014, date last accessed)
-
- Reynaud F, Giraud P, Cisterne J-M. et al. Acute immuno-allergic interstitial nephritis after treatment with fluindione. Seven cases. Néphrol Thér 2009; 5: 292–298 - PubMed
-
- Cam G, Kwetcheu AT, Vigneau C. et al. Acute and chronic nephropathy induced by fluindione must be addressed. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012; 27: 1554–1558 - PubMed
-
- Abt AB, Carroll LE, Mohler JH.. Thin basement membrane disease and acute renal failure secondary to gross hematuria and tubular necrosis. Am J Kidney Dis 2000; 35: 533–536 - PubMed
-
- August C, Atzeni A, Köster L. et al. Acute renal failure in IgA nephropathy: aggravation by gross hematuria due to anticoagulant treatment. J Nephrol 2002; 15: 709–712 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

