Targeting the vasculature in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: Starving versus normalizing blood supply
- PMID: 28617447
- PMCID: PMC5518951
- DOI: 10.1038/ctg.2017.28
Targeting the vasculature in hepatocellular carcinoma treatment: Starving versus normalizing blood supply
Abstract
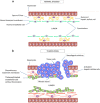
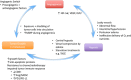
Traditional treatments for intermediate or advanced stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and anti-angiogenesis therapies were developed to starve tumor blood supply. A new approach of normalizing structurally and functionally abnormal tumor vasculature is emerging. While TACE improves survival in selected patients, the resulting tumor hypoxia stimulates proliferation, angiogenesis, treatment resistance and metastasis, which limits its overall efficacy. Vessel normalization decreases hypoxia and improves anti-tumor immune infiltrate and drug delivery. Several pre-clinical agents aimed at normalizing tumor vasculature in HCC appear promising. Although anti-angiogenic agents with vessel normalizing potential have been trialed in advanced HCC with modest results, to date their primary intention had been to starve the tumor. Judicious use of anti-angiogenic therapies is required to achieve vessel normalization yet avoid excessive pruning of vessels. This balance, termed the normalization window, is yet uncharacterized in HCC. However, the optimal class, dose and schedule of vascular normalization agents, alone or in combination with other therapies needs to be explored further.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have read and approved the final version.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Ervik M et al. GLOBOCAN 2012 v10, Cancer Incidence and Mortality Worldwide: IARC CancerBase No 11 [Internet] International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2013. Available at http://globocan.iarc.fr/. Accessed on 5 February 2017.
-
- Okuda K, Ohtsuki T, Obata H et al. Natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma and prognosis in relation to treatment. Study of 850 patients. Cancer 1985; 56: 918–928. - PubMed
-
- The Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) Investigators. A new prognostic system for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study of 435 patients: the Cancer of the Liver Italian Program (CLIP) investigators. Hepatology 1998; 28: 751–755. - PubMed
-
- Takayama T, Makuuchi M, Kojiro M et al. Early hepatocellular carcinoma: pathology, imaging, and therapy. Ann Surg Oncol 2008; 15: 972–978. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Llovet JM. Prognostic prediction and treatment strategy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2002; 35: 519–524. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

