Integrated pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) model to evaluate the in vivo antimicrobial activity of Marbofloxacin against Pasteurella multocida in piglets
- PMID: 28619095
- PMCID: PMC5471993
- DOI: 10.1186/s12917-017-1099-z
Integrated pharmacokinetic-Pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) model to evaluate the in vivo antimicrobial activity of Marbofloxacin against Pasteurella multocida in piglets
Abstract
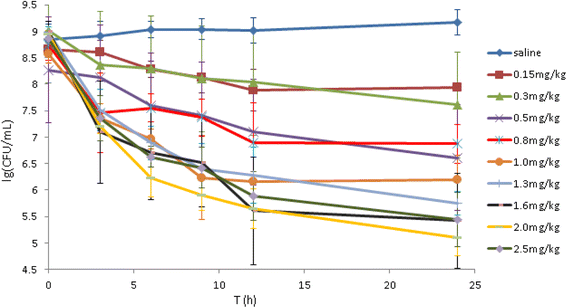
Background: Marbofloxacin is a veterinary fluoroquinolone with high activity against Pasteurella multocida. We evaluated it's in vivo activity against P. multocida based on in vivo time-kill data in swine using a tissue-cage model. A series of dosages ranging from 0.15 to 2.5 mg/kg were administered intramuscularly after challenge with P. multocida type B, serotype 2.
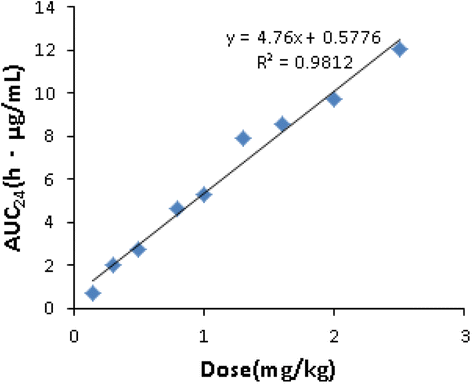
Results: The ratio of the 24 h area under the concentration-time curve divided by the minimum inhibitory concentration (AUC24TCF/MIC) was the best PK/PD index correlated with the in vivo antibacterial effectiveness of marbofloxacin (R2 = 0.9279). The AUC24TCF/MIC necessary to achieve a 1-log10 CFU/ml reduction and a 3-log10 CFU/ml (90% of the maximum response) reduction as calculated by an inhibitory sigmoid Emax model were 13.48 h and 57.70 h, respectively.
Conclusions: Marbofloxacin is adequate for the treatment of swine infected with P. multocida. The tissue-cage model played a significant role in achieving these PK/PD results.
Keywords: Marbofloxacin; P. Multocida; PK/PD; Piglets; Tissue-cage model.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

