Dl-3-n-butylphthalide protects the heart against ischemic injury and H9c2 cardiomyoblasts against oxidative stress: involvement of mitochondrial function and biogenesis
- PMID: 28619102
- PMCID: PMC5471652
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-017-0345-9
Dl-3-n-butylphthalide protects the heart against ischemic injury and H9c2 cardiomyoblasts against oxidative stress: involvement of mitochondrial function and biogenesis
Abstract
Background: Myocardial infarction (MI) is an acute and fatal condition that threatens human health. Dl-3-n-butylphthalide (NBP) has been used for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Mitochondria may play a protective role in MI injury. However, there are few reports on the cardioprotective effect of NBP or the potential mitochondrial mechanism for the NBP-induced protection against cardiac ischemia injury. We investigated the therapeutic effects of NBP in an in vivo MI model and an in vitro oxidative stress model, as well as the potential mitochondrial mechanism.
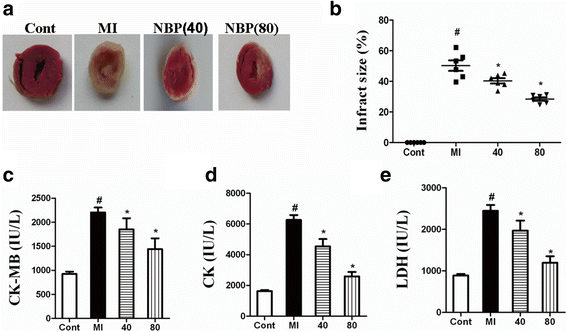
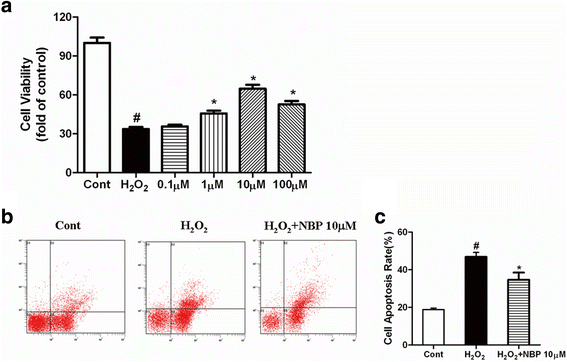
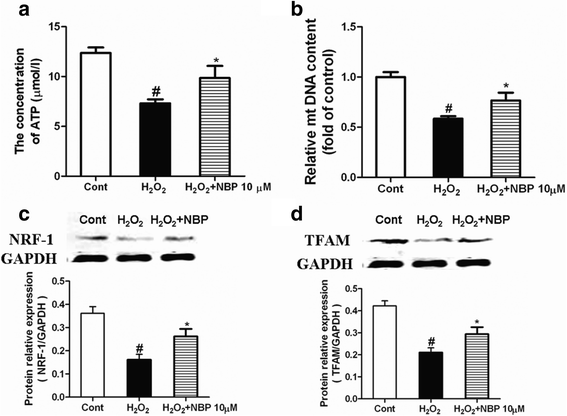
Methods: This study comprised two different experiments. The aim of experiment 1 was to determine the protective effects of NBP on MI and the underlying mechanisms in vivo. In part 1, myocardial infarct size was measured by staining with 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazoliumchloride (TTC). Myocardial enzymes and mitochondrial enzymes were assayed. The aim of experiment 2 was to investigate the role of NBP in H2O2-induced myocardial ischemic injury in H9c2 cells and to determine the potential mechanism. In part 2, H9c2 cell viability was evaluated. ROS levels, mitochondrial morphology, and mitochondrial membrane potential of H9c2 cells were measured. ATP levels were evaluated using an assay kit; mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA), the expressions of NRF-1 and TFAM, and mitochondrial biogenesis factors were determined.
Results: NBP treatment significantly reduced the infarct ratio, as observed by TTC staining, decreased serum myocardial enzymes in MI, and restored heart mitochondrial enzymes (isocitrate dehydrogenase (ICDH), succinate dehydrogenase (SDH), malate dehydrogenase (MDH), and a-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (a-KGDH) activities after MI. Moreover, in in vitro studies, NBP significantly increased the viability of H9c2 cells in a dose-dependent manner, reduced cell apoptosis, protected mitochondrial functions, elevated the cellular ATP levels, and promoted H2O2-induced mitochondrial biogenesis in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts.
Conclusion: Collectively, the results from both the in vivo and in vitro experiments suggested that NBP exerted a cardioprotective effect on cardiac ischemic injury via the regulation of mitochondrial function and biogenesis.
Keywords: Dl-3-n-butylphthalide; Mitochondrial biogenesis; Mitochondrial function; Myocardial infarction.
Figures



Similar articles
-
DL-3-n-butylphthalide protects endothelial cells against oxidative/nitrosative stress, mitochondrial damage and subsequent cell death after oxygen glucose deprivation in vitro.Brain Res. 2009 Sep 22;1290:91-101. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.07.020. Epub 2009 Jul 16. Brain Res. 2009. PMID: 19616517
-
Araloside C protects H9c2 cardiomyoblasts against oxidative stress via the modulation of mitochondrial function.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Sep;117:109143. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109143. Epub 2019 Jul 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31387189
-
DL-3-n-butylphthalide Protected Retinal Müller Cells Dysfunction from Oxidative Stress.Curr Eye Res. 2019 Oct;44(10):1112-1120. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2019.1624777. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Curr Eye Res. 2019. PMID: 31188648
-
Application and prospects of butylphthalide for the treatment of neurologic diseases.Chin Med J (Engl). 2019 Jun 20;132(12):1467-1477. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000289. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019. PMID: 31205106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dl-3-n-Butylphthalide (NBP): A Promising Therapeutic Agent for Ischemic Stroke.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2018;17(5):338-347. doi: 10.2174/1871527317666180612125843. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 29895257 Review.
Cited by
-
Dl-3-n-butylphthalide attenuates myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury by suppressing oxidative stress and regulating cardiac mitophagy via the PINK1/Parkin pathway in rats.J Thorac Dis. 2022 May;14(5):1651-1662. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-585. J Thorac Dis. 2022. PMID: 35693588 Free PMC article.
-
Rosuvastatin Improves Neurite Outgrowth of Cortical Neurons against Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation via Notch1-mediated Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Functional Improvement.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Jan 17;12:6. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00006. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29387001 Free PMC article.
-
DL-3-n-butylphthalide attenuates doxorubicin-induced acute cardiotoxicity via Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 6;10(5):e27644. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27644. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38486757 Free PMC article.
-
Honokiol ameliorates oxidative stress-induced DNA damage and apoptosis of c2c12 myoblasts by ROS generation and mitochondrial pathway.Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2019 Dec 28;24(1):60-68. doi: 10.1080/19768354.2019.1706634. eCollection 2020. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 2019. PMID: 32158617 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective Effects of dl-3-n-Butylphthalide against Doxorubicin-Induced Neuroinflammation, Oxidative Stress, Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, and Behavioral Changes.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Aug 16;2018:9125601. doi: 10.1155/2018/9125601. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 30186550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen O, Ye Z, Cao Z, Manaenko A, Ning K, Zhai X, Zhang R, Zhang T, Chen X, Liu W, Sun X. Methane attenuates myocardial ischemia injury in rats through anti-oxidative, anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory actions. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;90:1–11. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.11.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pei H, Song X, Peng C, Tan Y, Li Y, Li X, Ma S, Wang Q, Huang R, Yang D, Li D, Gao E, Yang Y. TNF-α inhibitor protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via Notch1-mediated suppression of oxidative/nitrative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;82:114–121. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2015.02.002. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang XM, Cui L, White J, Kuck J, Ruchko MV, Wilson GL, Alexeyev M, Gillespie MN, Downey JM, Cohen MV. Mitochondrially targeted Endonuclease III has a powerful anti-infarct effect in an in vivo rat model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion. Basic Res Cardiol. 2015;110(2):3. doi: 10.1007/s00395-014-0459-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

