Effect of community health clubs on child diarrhoea in western Rwanda: cluster-randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 28619228
- PMCID: PMC5561270
- DOI: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30217-6
Effect of community health clubs on child diarrhoea in western Rwanda: cluster-randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Community health clubs are multi-session village-level gatherings led by trained facilitators and designed to promote healthy behaviours mainly related to water, sanitation, and hygiene. They have been implemented in several African and Asian countries but have never been evaluated rigorously. We aimed to evaluate the effect of two versions of the community health club model on child health and nutrition outcomes.
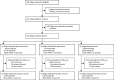
Methods: We did a cluster-randomised trial in Rusizi district, western Rwanda. We defined villages as clusters. We assessed villages for eligibility then randomly selected 150 for the study using a simple random sampling routine in Stata. We stratified villages by wealth index and by the proportion of children younger than 2 years with caregiver-reported diarrhoea within the past 7 days. We randomly allocated these villages to three study groups: no intervention (control; n=50), eight community health club sessions (Lite intervention; n=50), or 20 community health club sessions (Classic intervention; n=50). Households in these villages were enrolled in 2013 for a baseline survey, then re-enrolled in 2015 for an endline survey. The primary outcome was caregiver-reported diarrhoea within the previous 7 days in children younger than 5 years. Analysis was by intention to treat and per protocol. This trial is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT01836731.
Findings: At the baseline survey undertaken between May, 2013, and August, 2013, 8734 households with children younger than 5 years of age were enrolled. At the endline survey undertaken between Sept 21, 2015, and Dec 22, 2015, 7934 (91%) of the households were re-enrolled. Among children younger than 5 years, the prevalence of caregiver-reported diarrhoea in the previous 7 days was 514 (14%) of 3616 assigned the control, 453 (14%) of 3196 allocated the Lite intervention (prevalence ratio compared with control 0·97, 95% CI 0·81-1·16; p=0·74), and 495 (14%) of 3464 assigned the Classic intervention (prevalence ratio compared with control 0·99, 0·85-1·15; p=0·87).
Interpretation: Community health clubs, in this setting in western Rwanda, had no effect on caregiver-reported diarrhoea among children younger than 5 years. Our results question the value of implementing this intervention at scale for the aim of achieving health gains.
Funding: Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Positive steps with negative studies in the WASH sector.Lancet Glob Health. 2017 Jul;5(7):e642-e643. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30221-8. Lancet Glob Health. 2017. PMID: 28619213 No abstract available.
References
-
- United Nations . Sustainable development goals. Sept 25, 2015. http://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/sustainable-development-goals/ (accessed Jan 25, 2017)
-
- UNICEF . Rwanda: common country programme document 2013–2018. June 21, 2013. http://www.unicef.org/about/execboard/files/2013-RWA1-Rwanda_CCPD-final_... (accessed May 22, 2015)
-
- United States Agency for International Development (USAID) Rwanda: nutrition profile. June, 2014. https://www.usaid.gov/sites/default/files/documents/1864/USAID-Rwanda_NC... (accessed June 23, 2015)
-
- National Institute of Statistics of Rwanda, Ministry of Finance and Economic Planning, Ministry of Health, ICF International . Rwanda demographic and health survey 2014–15. March, 2016. https://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/FR316/FR316.pdf (accessed May 9, 2017)
-
- Ministry of Health of Rwanda . Roadmap for CBEHPP. Ministry of Health, Environmental Health Desk; Kigali: 2010.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous