Cocaine adulteration
- PMID: 28619473
- PMCID: PMC7610562
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2017.06.001
Cocaine adulteration
Abstract
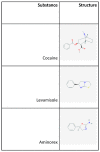
Cocaine is a naturally occurring and illicitly used psychostimulant drug. Cocaine acts at monoaminergic neurotransmitter transporters to block uptake of the monoamines, dopamine, serotonin and norepinephrine. The resulting increase of monoamines in the extracellular space underlies the positively reinforcing effects that cocaine users seek. In turn, this increase in monoamines underlies the development of addiction, and can also result in a number of severe side effects. Currently, cocaine is one of the most common illicit drugs available on the European market. However, cocaine is increasingly sold in impure forms. This trend is driven by cocaine dealers seeking to increase their profit margin by mixing ("cutting") cocaine with numerous other compounds ("adulterants"). Importantly, these undeclared compounds put cocaine consumers at risk, because consumers are not aware of the additional potential threats to their health. This review describes adulterants that have been identified in cocaine sold on the street market. Their typical pharmacological profile and possible reasons why these compounds can be used as cutting agents will be discussed. Since a subset of these adulterants has been found to exert effects similar to cocaine itself, we will discuss levamisole, the most frequently used cocaine cutting agent today, and its metabolite aminorex.
Keywords: Adulterant; Aminorex; Cocaine; Levamisole; Neurotransmitter transporter.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no competing financial interests related to the publication of this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Barker SA. The formation of aminorex in racehorses following levamisole administration: a quantitative and chiral analysis following synthetic aminorex or levamisole administration vs. aminorex-positive samples from the field: a preliminary report. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2009;32:160–166. - PubMed
-
- Baumann MH, Partilla JS, Lehner KR, Thorndike EB, Hoffman AF, Holy M, Rothman RB, Goldberg SR, Lupica CR, Sitte HH, Brandt SD, et al. Powerful cocaine-like actions of 3,4-Methylenedioxypyrovalerone (MDPV), a principal constituent of psychoactive ‘Bath salts’ products. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013b;38:552–562. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bertol E, Mari F, Milia MG, Politi L, Furlanetto S, Karch SB. Determination of aminorex in human urine samples by GC–MS after use of levamisole. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011;55:1186–1189. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

