The inner blood-retinal barrier: Cellular basis and development
- PMID: 28619516
- PMCID: PMC5723228
- DOI: 10.1016/j.visres.2017.05.009
The inner blood-retinal barrier: Cellular basis and development
Abstract
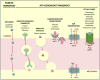
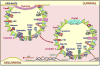
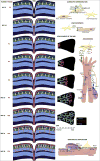
The blood-retinal barrier (BRB) regulates transport across retinal capillaries maintaining proper neural homeostasis and protecting the neural tissue from potential blood borne toxicity. Loss of the BRB contributes to the pathophysiology of a number of blinding retinal diseases including diabetic retinopathy. In this review, we address the basis of the BRB, including the molecular mechanisms that regulate flux across the retinal vascular bed. The routes of transcellular and paracellular flux are described as well as alterations in these pathways in response to permeabilizing agents in diabetes. Finally, we provide information on exciting new studies that help to elucidate the process of BRB development or barriergenesis and how understanding this process may lead to new opportunities for barrier restoration in diabetic retinopathy.
Keywords: Barriergenesis; Blood-retinal barrier; Paracellular permeability; Tight junctions; Transcytosis.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Alvarez JI, Dodelet-Devillers A, Kebir H, Ifergan I, Fabre PJ, Terouz S, Sabbagh M, Wosik K, Bourbonniere L, Bernard M, van Horssen J, de Vries HE, Charron F, Prat A. The Hedgehog pathway promotes blood-brain barrier integrity and CNS immune quiescence. Science. 2011;334(6063):1727–1731. - PubMed
-
- Anderson KD, Pan L, Yang XM, Hughes VC, Walls JR, Dominguez MG, Simmons MV, Burfeind P, Xue Y, Wei Y, Macdonald LE, Thurston G, Daly C, Lin HC, Economides AN, Valenzuela DM, Murphy AJ, Yancopoulos GD, Gale NW. Angiogenic sprouting into neural tissue requires Gpr124, an orphan G protein-coupled receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(7):2807–2812. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

