Recording sympathetic nerve activity from the skin
- PMID: 28619579
- PMCID: PMC5753603
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2017.05.003
Recording sympathetic nerve activity from the skin
Abstract
Sympathetic tone is important in cardiac arrhythmogenesis; however, methods to estimate sympathetic tone are either invasive or require proper sinus node function that may be abnormal in disease states. Because of the direct and extensive connections among various nerve structures, it is possible for the sympathetic nerves in the various structures to activate simultaneously. Therefore, we hypothesized that nerve activity can be recorded from the skin and it can be used to estimate the cardiac sympathetic tone. Preclinical studies in canines demonstrated that nerve activity is detectable using conventional ECG electrodes and can be used to estimate cardiac sympathetic tone. Subsequent clinical studies further supported this concept. In addition to studying the autonomic mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmia, these new methods may have broad application in studying both cardiac and non-cardiac diseases.
Keywords: Arrhythmia; Autonomic nervous system; Sympathetic nerve activity.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

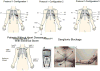




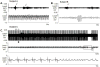

Comment in
-
Editorial Commentary: Tuning in to sympathetic activity cutaneously in humans-A bench to bedside saga.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2017 Oct;27(7):473-474. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2017.06.004. Epub 2017 Jun 9. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2017. PMID: 28709809 No abstract available.
References
-
- Einthoven W. Galvanometrische registratie van het menschelijk electrocardiogram. Leiden, Netherlands: Eduard Ijdo; 1902.
-
- Shen MJ, Choi EK, Tan AY, Lin SF, Fishbein MC, Chen LS, et al. Neural mechanisms of atrial arrhythmias. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2011;27:30–9. - PubMed
-
- Mark AL, Wallin BG. Microneurography: a technique for assessing central neural effects of adrenergic drugs on sympathetic outflow in humans. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 1985;7(Suppl 8):S67–9. - PubMed
-
- Vallbo AB, Hagbarth KE, Wallin BG. Microneurography: how the technique developed and its role in the investigation of the sympathetic nervous system. JApplPhysiol. 2004;96(4):1262–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

