Herbal medicine (Hyeolbuchukeo-tang or Xuefu Zhuyu decoction) for treating primary dysmenorrhoea: protocol for a systematic review of randomised controlled trials
- PMID: 28619773
- PMCID: PMC5623393
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-015056
Herbal medicine (Hyeolbuchukeo-tang or Xuefu Zhuyu decoction) for treating primary dysmenorrhoea: protocol for a systematic review of randomised controlled trials
Abstract
Introduction: Primary dysmenorrhoea is menstrual pain without pelvic pathology and is the most common gynaecological condition in women. Xuefu Zhuyudecoction (XZD) or Hyeolbuchukeo-tang, a traditional herbal formula, has been used as a treatment for primary dysmenorrhoea. The purpose of this study is to assess the current published evidence regarding XZD as treatment for primary dysmenorrhoea.
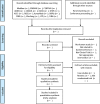
Materials and methods: The following databases will be searched from their inception until April 2017: MEDLINE (via PubMed), Allied and Complementary Medicine Database (AMED), EMBASE, The Cochrane Library, six Korean medical databases (Korean Studies Information Service System, DBPia, Oriental Medicine Advanced Searching Integrated System, Research Information Service System, Korea Med and the Korean Traditional Knowledge Portal), three Chinese medical databases (China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Wan Fang Database and Chinese Scientific Journals Database (VIP)) and one Japanese medical database (CiNii). Randomised clinical trials (RCTs) that will be included in this systematic review comprise those that used XZD or modified XZD. The control groups in the RCTs include no treatment, placebo, conventional medication or other treatments. Trials testing XZD as an adjunct to other treatments and studies where the control group received the same treatment as the intervention group will be also included. Data extraction and risk of bias assessments will be performed by two independent reviewers. The risk of bias will be assessed with the Cochrane risk of bias tool. All statistical analyses will be conducted using Review Manager software (RevMan V.5.3.0).
Ethics and dissemination: This systematic review will be published in a peer-reviewed journal. The review will also be disseminated electronically and in print. The review will benefit patients and practitioners in the fields of traditional and conventional medicine.
Prospero registration number: CRD42016050447.
Keywords: Herbal medicine; dysmenorrhoea; protocol; systematic review.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2017. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Herbal medicine (Hyeolbuchukeo-tang or Xuefu Zhuyu decoction) for treating primary dysmenorrhea: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Feb;98(5):e14170. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014170. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30702569 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal medicine Shaofu Zhuyu decoction for primary dysmenorrhea: a systematic review protocol.Syst Rev. 2016 Jan 20;5:9. doi: 10.1186/s13643-016-0185-9. Syst Rev. 2016. PMID: 26786509 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal medicine Yukgunja-tang for functional dyspepsia protocol for a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Oct;97(40):e12555. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012555. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30290614 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal medicine Banha-sasim-tang for the treatment of functional dyspepsia protocol for a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 May;98(22):e15760. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015760. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 31145294 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal medicine (Taohong Siwu Tang) for the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Explore (NY). 2020 Sep-Oct;16(5):297-303. doi: 10.1016/j.explore.2020.05.013. Epub 2020 Jul 9. Explore (NY). 2020. PMID: 32723605
Cited by
-
Effectiveness of Shenshu Guanxin recipe granules for improving exercise tolerance in patients with stable angina pectoris: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.J Tradit Chin Med. 2023 Oct;43(6):1227-1233. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20231008.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2023. PMID: 37946485 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Direct Relationship Between 'Blood Stasis' and Fibrinaloid Microclots in Chronic, Inflammatory, and Vascular Diseases, and Some Traditional Natural Products Approaches to Treatment.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 12;18(5):712. doi: 10.3390/ph18050712. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moxibustion for primary dysmenorrhea: Protocol for a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jan;99(1):e18547. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018547. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 31895793 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of prototype compounds and their metabolites in rats' serum from Xuefu Zhuyu Decoction by UPLC-Q-TOF/MS.Chin Herb Med. 2022 Sep 20;15(1):139-150. doi: 10.1016/j.chmed.2022.08.002. eCollection 2023 Jan. Chin Herb Med. 2022. PMID: 36875444 Free PMC article.
-
Herbal medicine (Hyeolbuchukeo-tang or Xuefu Zhuyu decoction) for treating primary dysmenorrhea: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2019 Feb;98(5):e14170. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014170. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019. PMID: 30702569 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Marjoribanks J, Ayeleke RO, Farquhar C, et al. . Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for dysmenorrhoea. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2015;7:Cd001751 doi:0.1002/14651858.CD001751.pub2. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
