Codependence of Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptor 2 and Transforming Growth Factor-β in Elastic Fiber Assembly and Its Perturbation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- PMID: 28619995
- PMCID: PMC5593082
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309696
Codependence of Bone Morphogenetic Protein Receptor 2 and Transforming Growth Factor-β in Elastic Fiber Assembly and Its Perturbation in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
Objective: We determined in patients with pulmonary arterial (PA) hypertension (PAH) whether in addition to increased production of elastase by PA smooth muscle cells previously reported, PA elastic fibers are susceptible to degradation because of their abnormal assembly.
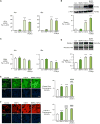
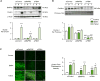
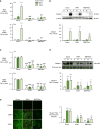
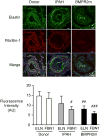
Approach and results: Fibrillin-1 and elastin are the major components of elastic fibers, and fibrillin-1 binds bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and the large latent complex of transforming growth factor-β1 (TGFβ1). Thus, we considered whether BMPs like TGFβ1 contribute to elastic fiber assembly and whether this process is perturbed in PAH particularly when the BMP receptor, BMPR2, is mutant. We also assessed whether in mice with Bmpr2/1a compound heterozygosity, elastic fibers are susceptible to degradation. In PA smooth muscle cells and adventitial fibroblasts, TGFβ1 increased elastin mRNA, but the elevation in elastin protein was dependent on BMPR2; TGFβ1 and BMP4, via BMPR2, increased extracellular accumulation of fibrillin-1. Both BMP4- and TGFβ1-stimulated elastic fiber assembly was impaired in idiopathic (I) PAH-PA adventitial fibroblast versus control cells, particularly those with hereditary (H) PAH and a BMPR2 mutation. This was related to profound reductions in elastin and fibrillin-1 mRNA. Elastin protein was increased in IPAH PA adventitial fibroblast by TGFβ1 but only minimally so in BMPR2 mutant cells. Fibrillin-1 protein increased only modestly in IPAH or HPAH PA adventitial fibroblasts stimulated with BMP4 or TGFβ1. In Bmpr2/1a heterozygote mice, reduced PA fibrillin-1 was associated with elastic fiber susceptibility to degradation and more severe pulmonary hypertension.
Conclusions: Disrupting BMPR2 impairs TGFβ1- and BMP4-mediated elastic fiber assembly and is of pathophysiologic significance in PAH.
Keywords: BMPR2 receptor; TGF-beta-1; elastin; fibrillin-1; fibroblasts; hypertension, pulmonary; smooth muscle cells.
© 2017 American Heart Association, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the co-authors have disclosures related to conflict of interest that influence the findings in this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Lane KB, Machado RD, Pauciulo MW, Thomson JR, Loyd JE, III, Nichols WC, Trembath RC. Heterozygous germline mutations in BMPR2, encoding a TGF-beta receptor, cause familial primary pulmonary hypertension. Nature Genetics. 2000;26:81–84. - PubMed
-
- Deng Z, Morse JH, Slager SL, Cuervo N, Moore KJ, Venetos G, Kalachikov S, Cayanis E, Fischer SG, Barst RJ, Hodge SE, Knowles JA. Familial primary pulmonary hypertension (gene pph1) is caused by mutations in the bone morphogenetic protein receptor-II gene. Am J Hum Genet. 2000;67:737–744. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atkinson C, Stewart S, Upton PD, Machado R, Thomson JR, Trembath RC, Morrell NW. Primary pulmonary hypertension is associated with reduced pulmonary vascular expression of type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor. Circulation. 2002;105:1672–1678. - PubMed
-
- Phillips JA, 3rd, Poling JS, Phillips CA, Stanton KC, Austin ED, Cogan JD, Wheeler L, Yu C, Newman JH, Dietz HC, Loyd JE. Synergistic heterozygosity for tgfbeta1 snps and BMPR2 mutations modulates the age at diagnosis and penetrance of familial pulmonary arterial hypertension. Genet Med. 2008;10:359–365. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

