Interleukin 17 Family Cytokines: Signaling Mechanisms, Biological Activities, and Therapeutic Implications
- PMID: 28620097
- PMCID: PMC5732092
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028522
Interleukin 17 Family Cytokines: Signaling Mechanisms, Biological Activities, and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
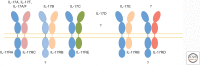
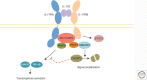
The cytokines of the interleukin 17 (IL-17) family play a central role in the control of infections, especially extracellular fungi. Conversely, if unrestrained, these inflammatory cytokines contribute to the pathology of numerous autoimmune and chronic inflammatory conditions. Recent advances have led to the approval of IL-17A-blocking biologics for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, but much remains to be understood about the biological functions, regulation, and signaling pathways downstream of these factors. In this review, we outline the current knowledge of signal transduction and known physiological activities of IL-17 family cytokines. We will highlight in particular the current understanding of these cytokines in the context of skin manifestations of disease.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Acosta-Rodriguez EV, Rivino L, Geginat J, Jarrossay D, Gattorno M, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F, Napolitani G. 2007. Surface phenotype and antigenic specificity of human interleukin 17-producing T helper memory cells. Nat Immunol 8: 639–646. - PubMed
-
- Aggarwal S, Gurney AL. 2002. IL-17: Prototype member of an emerging cytokine family. J Leukoc Biol 71: 1–8. - PubMed
-
- Aktar MK, Kido-Nakahara M, Furue M, Nakahara T. 2015. Mutual upregulation of endothelin-1 and IL-25 in atopic dermatitis. Allergy 70: 846–854. - PubMed
-
- Albanesi C, Cavani A, Girolomoni G. 1999. IL-17 is produced by nickel-specific T lymphocytes and regulates ICAM-1 expression and chemokine production in human keratinocytes: Synergistic or antagonist effects with IFN-γ and TNF-α. J Immunol 162: 494–502. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
