Cytokine Signaling in the Development and Homeostasis of Regulatory T cells
- PMID: 28620098
- PMCID: PMC5830895
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028597
Cytokine Signaling in the Development and Homeostasis of Regulatory T cells
Abstract
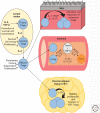
Cytokine signaling is indispensable for regulatory T-cell (Treg) development in the thymus, and also influences the homeostasis, phenotypic diversity, and function of Tregs in the periphery. Because Tregs are required for establishment and maintenance of immunological self-tolerance, investigating the role of cytokines in Treg biology carries therapeutic potential in the context of autoimmune disease. This review discusses the potent and diverse influences of interleukin (IL)-2 signaling on the Treg compartment, an area of knowledge that has led to the use of low-dose IL-2 as a therapy to reregulate autoaggressive immune responses. Evidence suggesting Treg-specific impacts of the cytokines transforming growth factor β (TGF-β), IL-7, thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), IL-15, and IL-33 is also presented. Finally, we consider the technical challenges and knowledge limitations that must be overcome to bring other cytokine-based, Treg-targeted therapies into clinical use.
Copyright © 2018 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Alpdogan O, van den Brink MR. 2005. IL-7 and IL-15: Therapeutic cytokines for immunodeficiency. Trends Immunol 26: 56–64. - PubMed
-
- Aoki CA, Borchers AT, Li M, Flavell RA, Bowlus CL, Ansari AA, Gershwin ME. 2005. Transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) and autoimmunity. Autoimmun Rev 4: 450–459. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
