A hot water extract of turmeric (Curcuma longa) suppresses acute ethanol-induced liver injury in mice by inhibiting hepatic oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine production
- PMID: 28620478
- PMCID: PMC5465857
- DOI: 10.1017/jns.2016.43
A hot water extract of turmeric (Curcuma longa) suppresses acute ethanol-induced liver injury in mice by inhibiting hepatic oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine production
Abstract
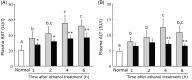
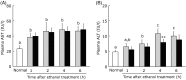
Turmeric (Curcuma longa) is a widely used spice that has various biological effects, and aqueous extracts of turmeric exhibit potent antioxidant activity and anti-inflammatory activity. Bisacurone, a component of turmeric extract, is known to have similar effects. Oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokines play an important role in ethanol-induced liver injury. This study was performed to evaluate the influence of a hot water extract of C. longa (WEC) or bisacurone on acute ethanol-induced liver injury. C57BL/6 mice were orally administered WEC (20 mg/kg body weight; BW) or bisacurone (60 µg/kg BW) at 30 min before a single dose of ethanol was given by oral administration (3·0 g/kg BW). Plasma levels of aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase were markedly increased in ethanol-treated mice, while the increase of these enzymes was significantly suppressed by prior administration of WEC. The increase of alanine aminotransferase was also significantly suppressed by pretreatment with bisacurone. Compared with control mice, animals given WEC had higher hepatic tissue levels of superoxide dismutase and glutathione, as well as lower hepatic tissue levels of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances, TNF-α protein and IL-6 mRNA. These results suggest that oral administration of WEC may have a protective effect against ethanol-induced liver injury by suppressing hepatic oxidation and inflammation, at least partly through the effects of bisacurone.
Keywords: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; BW, body weight; Bisacurone; Ethanol-induced liver injury; GSH, glutathione; GSSG, oxidised glutathione; Inflammatory cytokines; O2•−, superoxide anion radical; Oxidative stress; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SOD, superoxide dismutase; TBARS, thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances; Turmeric (Curcuma longa); WEC, hot water extract of Curcuma longa.
Figures




References
-
- Galicia-Moreno M & Gutierrez-Reyes G (2014) The role of oxidative stress in the development of alcoholic liver disease. Rev Gastroenterol Mex 79, 135–144. - PubMed
-
- Gonzalez J, Munoz ME, Martin MI, et al. (1988) Influence of acute ethanol administration on hepatic glutathione metabolism in the rat. Alcohol 5, 103–106. - PubMed
-
- Ribiere C, Sinaceur J, Sabourault D, et al. (1985) Hepatic catalase and superoxide dismutases after acute ethanol administration in rats. Alcohol 2, 31–33. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

