Postprandial metabolic response of breast-fed infants and infants fed lactose-free vs regular infant formula: A randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 28623320
- PMCID: PMC5473881
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-03975-4
Postprandial metabolic response of breast-fed infants and infants fed lactose-free vs regular infant formula: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
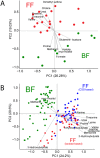
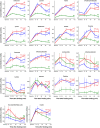
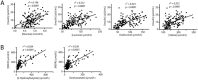
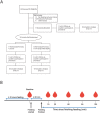
Lactose intolerance is a major concern driving the growth of lactose-free foods including lactose-free infant formula. It is unknown what the metabolic consequence is of consumption of a formula where lactose has been replaced with corn syrup solids (CSS). Here, a randomized double-blinded intervention study was conducted where exclusively formula-fed infants were fed formula containing either lactose or CSS-based infant formula and compared with an equal number of exclusively breast-fed infants. Plasma metabolites and insulin were measured at baseline, 15, 30, 60, 90 and 120 min after feeding. Differences in plasma metabolite profiles for formula-fed infants included a rapid increase in circulating amino acids, creatinine and urea compared with breast-fed infants. At 120 min post-feeding, insulin was significantly elevated in formula-fed compared with breast-fed infants. Infants fed lactose-based formula had the highest levels of glucose at 120 min, and leucine, isoleucine, valine and proline at 90 and 120 min, whereas infants fed CSS-based formula had the lowest levels of non-esterified fatty acids at all time points, and glucose at 120 min. Overall, these differences highlight that changes in infant formula composition impact infant metabolism, and show that metabolomics is a powerful tool to help with development of improved infant formulas.
Conflict of interest statement
Slupsky, He, West and Andersson declare no competing interests. Rudolph is an employee of Mead Johnson. Hernell and Lönnerdal have received research grants from Mead Johnson Nutrition and honoraria for lectures at symposia. All research support was paid to Umeå University and the University of California, Davis.
Figures
References
-
- Schaafsma G. Lactose and lactose derivatives as bioactive ingredients in human nutrition. Int Dairy J. 2008;28:458–465. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2007.11.013. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

