Is the hydrophobic core a universal structural element in proteins?
- PMID: 28623601
- PMCID: PMC5487895
- DOI: 10.1007/s00894-017-3367-z
Is the hydrophobic core a universal structural element in proteins?
Abstract
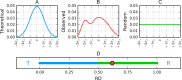
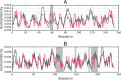
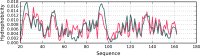
The hydrophobic core, when subjected to analysis based on the fuzzy oil drop model, appears to be a universal structural component of proteins irrespective of their secondary, supersecondary, and tertiary conformations. A study has been performed on a set of nonhomologous proteins representing a variety of CATH categories. The presence of a well-ordered hydrophobic core has been confirmed in each case, regardless of the protein's biological function, chain length or source organism. In light of fuzzy oil drop (FOD) analysis, various supersecondary forms seem to share a common structural factor in the form of a hydrophobic core, emerging either as part of the whole protein or a specific domain. The variable status of individual folds with respect to the FOD model reflects their propensity for conformational changes, frequently associated with biological function. Such flexibility is expressed as variable stability of the hydrophobic core, along with specific encoding of potential conformational changes which depend on the properties of helices and β-folds.
Keywords: Hydrophobic core; Hydrophobicity; Protein folding.
Figures








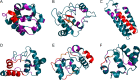
Similar articles
-
The Amyloid as a Ribbon-Like Micelle in Contrast to Spherical Micelles Represented by Globular Proteins.Molecules. 2019 Dec 3;24(23):4395. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234395. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31816829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Secondary and Supersecondary Structure of Proteins in Light of the Structure of Hydrophobic Cores.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1958:347-378. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9161-7_19. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30945229
-
The fuzzy oil drop model, based on hydrophobicity density distribution, generalizes the influence of water environment on protein structure and function.J Theor Biol. 2014 Oct 21;359:6-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2014.05.007. Epub 2014 May 21. J Theor Biol. 2014. PMID: 24859428
-
Hydrophobic core formation in protein complex of cathepsin.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2014;32(7):1023-32. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2013.801784. Epub 2013 Jul 5. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2014. PMID: 23826628
-
Marginally hydrophobic transmembrane α-helices shaping membrane protein folding.Protein Sci. 2015 Jul;24(7):1057-74. doi: 10.1002/pro.2698. Epub 2015 May 30. Protein Sci. 2015. PMID: 25970811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The functions and regulation of heat shock proteins; key orchestrators of proteostasis and the heat shock response.Arch Toxicol. 2021 Jun;95(6):1943-1970. doi: 10.1007/s00204-021-03070-8. Epub 2021 May 18. Arch Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 34003342 Review.
-
External Force Field for Protein Folding in Chaperonins-Potential Application in In Silico Protein Folding.ACS Omega. 2024 Apr 10;9(16):18412-18428. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c00409. eCollection 2024 Apr 23. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38680295 Free PMC article.
-
Conformational changes in the catalytic region are responsible for heat-induced activation of hyperthermophilic homoserine dehydrogenase.Commun Biol. 2022 Jul 14;5(1):704. doi: 10.1038/s42003-022-03656-7. Commun Biol. 2022. PMID: 35835834 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in extracellular vesicles for therapeutic cargo delivery.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Apr;56(4):836-849. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01201-6. Epub 2024 Apr 1. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38556545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Amyloid as a Ribbon-Like Micelle in Contrast to Spherical Micelles Represented by Globular Proteins.Molecules. 2019 Dec 3;24(23):4395. doi: 10.3390/molecules24234395. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31816829 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Devlin TM. Textbook of biochemistry with clinical correlations. 7. New York: Wiley; 2011.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

