Roles of ST2, IL-33 and BNP in predicting major adverse cardiovascular events in acute myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention
- PMID: 28623858
- PMCID: PMC5661109
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13183
Roles of ST2, IL-33 and BNP in predicting major adverse cardiovascular events in acute myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention
Abstract
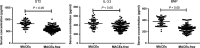
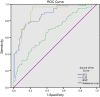
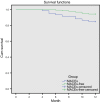
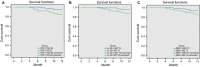
This study investigated roles of serum ST2, IL-33 and BNP in predicting major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Blood samples were collected from the included AMI patients (n = 180) who underwent PCI. All patients were divided into the MACEs and MACEs-free groups. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was performed to measure serum levels of ST2, IL-33 and BNP. Severity of coronary artery lesion was evaluated by Gensini score. Pearson correlation analysis was used. A receiver operating characteristics curve was drawn to evaluate the potential roles of ST2, IL-33 and BNP in predicting MACEs, and Kaplan-Meier curve to analyse the 1-year overall survival rate. Logistic regression analysis was conducted to analyse the independent risk factors for MACEs. Compared with the MACEs-free group, the serum levels of ST2, IL-33 and BNP were significantly higher in the MACEs group. Serum levels of ST2, IL-33 and BNP were positively correlated with each other and positively correlated with Gensini score. The area under curves of ST2, IL-33 and BNP, respectively, were 0.872, 0.675 and 0.902. The relative sensitivity and specificity were, respectively, 76.27% and 85.92%, 69.49% and 58.68%, as well as, 96.61% and 77.69%. Serum levels of ST2, IL-33 and BNP were independent risk factors for MACEs. The 1-year overall survival rate was higher in AMI patients with lower serum levels of ST2, IL-33 and BNP. In conclusion, serum levels of ST2, IL-33 and BNP have potential value in predicting MACEs in AMI patients undergoing PCI.
Keywords: BNP; Acute myocardial infarction; IL-33; Major adverse cardiovascular events; Percutaneous coronary intervention; ST2.
© 2017 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
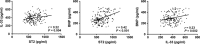
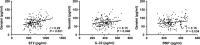
References
-
- Zhang K, Zhang XC, Mi YH, et al Predicting value of serum soluble ST2 and interleukin‐33 for risk stratification and prognosis in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Chin Med J (Engl). 2013; 126: 3628–31. - PubMed
-
- Fox KA, Goodman SG, Klein W, et al Management of acute coronary syndromes. Variations in practice and outcome; findings from the Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE). Eur Heart J. 2002; 23: 1177–89. - PubMed
-
- Kook HY, Jeong MH, Oh S, et al Current trend of acute myocardial infarction in Korea (from the Korea Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry from 2006 to 2013). Am J Cardiol. 2014; 114: 1817–22. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

