Early versus late initiation of renal replacement therapy impacts mortality in patients with acute kidney injury post cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 28623953
- PMCID: PMC5474059
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-017-1707-0
Early versus late initiation of renal replacement therapy impacts mortality in patients with acute kidney injury post cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Early versus late initiation of renal replacement therapy impacts mortality in patients with acute kidney injury post cardiac surgery: a meta-analysis.Crit Care. 2019 Apr 25;23(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s13054-018-2065-2. Crit Care. 2019. PMID: 31023324 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common clinical complication of cardiac surgery and increases mortality and hospitalization. We aimed to explore and perform an updated meta-analysis of qualitative and quantitative evaluations of the relationship between early renal replacement therapy (RRT) and mortality.
Methods: We searched the Chinese Biomedical Database, the Cochrane Library, EMBASE, Global Health, MEDLINE and PubMed.
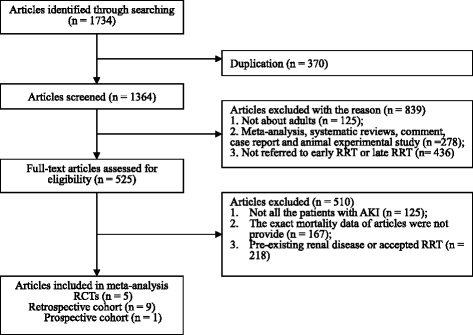
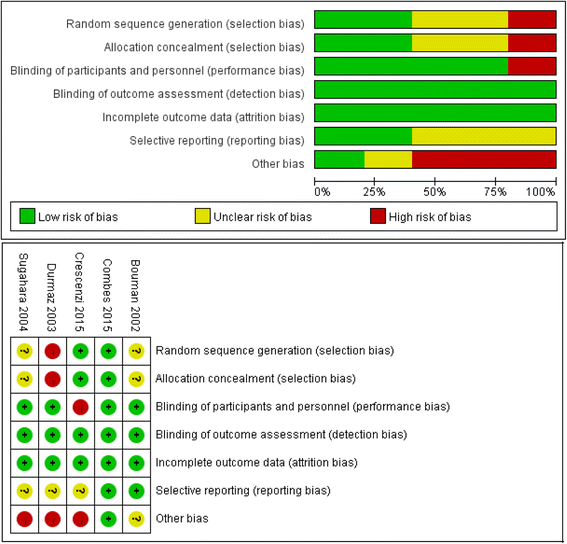
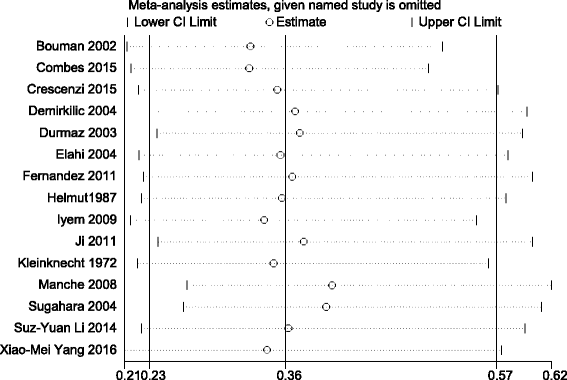
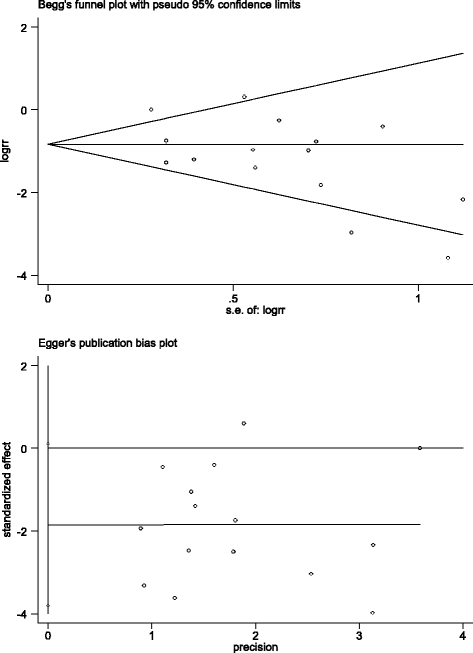
Results: Fifteen studies (five randomized controlled trials (RCTs), one prospective cohort and nine retrospective cohorts) including 1479 patients were identified for detailed evaluation. The meta-analysis suggested that early RRT initiation reduced 28-day mortality (odds ratio (OR) 0.36; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.23 to 0.57; I 2 60%), and shortened intensive care unit (ICU) length of stay (LOS) (mean difference (MD) -2.50; 95% CI -3.53 to -1.47; I 2 88%) and hospital LOS (MD -0.69; 95% CI -1.13 to -0.25; I 2 88%), and also reduced the duration of RRT (MD -1.18; 95% CI -2.26 to -0.11; I 2 69%), especially when RRT was initiated early within 12 hours (OR 0.23; 95% CI 0.08 to 0.63; I 2 73%) and within 24 hours (OR 0.52; 95% CI 0.28 to 0.95; I 2 58%) in patients with AKI after cardiac surgery.
Conclusions: Early RRT initiation decreased 28-day mortality, especially when it was started within 24 hours after cardiac surgery in patients with AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Cardiac surgery; Early; Mortality; Renal replacement therapy.
Figures

Comment in
-
Renal replacement therapy after cardiac surgery: do not ask "When", ask "Why".Crit Care. 2017 Sep 5;21(1):231. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1818-7. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28874172 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Accounting for single center effects in systematic reviews cannot be overlooked.Crit Care. 2017 Sep 15;21(1):241. doi: 10.1186/s13054-017-1804-0. Crit Care. 2017. PMID: 28915905 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cooper WA, O’Brien SM, Thourani VH, Guyton RA, Bridges CR, Szczech LA, et al. Impact of renal dysfunction on outcomes of coronary artery bypass surgery: results from the Society of Thoracic Surgeons National Adult Cardiac Database. Circulation. 2006;113:1063–70. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.580084. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

