Effects of Teriparatide, Denosumab, or Both on Spine Trabecular Microarchitecture in DATA-Switch: a Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 28624340
- PMCID: PMC5673584
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jocd.2017.05.007
Effects of Teriparatide, Denosumab, or Both on Spine Trabecular Microarchitecture in DATA-Switch: a Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
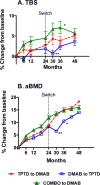
In postmenopausal women, 2 yr of combined teriparatide and denosumab increases bone mineral density more than either drug alone, and switching from either combination or teriparatide to denosumab for an additional 2 yr further increases bone mineral density. Conversely, switching from denosumab to teriparatide results in transient bone loss. The effects of these interventions on spine microarchitecture are unknown. In the DATA and DATA-Switch studies, 94 postmenopausal osteoporotic women were randomized to receive 24 mo of teriparatide (20 µg daily), denosumab (60 mg every 6 mo), or both. Then, women originally assigned to 24 mo of teriparatide received 24 mo of denosumab, whereas subjects originally randomized to 24 mo of denosumab received 24 mo of teriparatide. Subjects who received both drugs received an additional 24 mo of denosumab alone. Spine trabecular bone score (TBS, a gray-level textural assessment of bone microarchitecture) was measured blinded from treatment groups using images from 2-dimensional dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry spine scans at 0, 12, 24, 30, 36, and 48 mo in 65 women who had posterior-anterior spine dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry images suitable for TBS analysis. After 24 mo, TBS increased by 2.7 ± 4.7% in the teriparatide group (p = 0.009 vs baseline), by 1.8 ± 5.0% in the denosumab group (p = 0.118 vs baseline), and by 4.5 ± 6.7% in the combination group (p = 0.017 vs baseline), with no significant between-group differences. In the 6 mo after the treatments were switched (months 24-30), TBS continued to increase in the combination-to-denosumab and teriparatide-to-denosumab groups but decreased by -1.1 ± 4.0% in the denosumab-to-teriparatide group (p < 0.05 vs other groups). After 48 mo, compared to month 0, TBS increased by 5.1 ± 5.8% in the teriparatide-to-denosumab group, by 3.6 ± 4.2% in the denosumab-to-teriparatide group, and by 6.1 ± 4.7% in the combination-to-denosumab group (p < 0.001 vs baseline for all groups, p = not significant for between-group differences). Switching from teriparatide to denosumab also increased spine TBS. Conversely, switching from denosumab to teriparatide transiently degraded spine trabecular microarchitecture, the clinical consequences of which require further study.
Keywords: Denosumab; osteoporosis; teriparatide.
Copyright © 2017 The International Society for Clinical Densitometry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Delmas PD, Seeman E. Changes in bone mineral density explain little of the reduction in vertebral or nonvertebral fracture risk with anti-resorptive therapy. Bone. 2004;34:599–604. - PubMed
-
- Neer RM, Arnaud CD, Zanchetta JR, et al. Effect of parathyroid hormone (1–34) on fractures and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. The New England journal of medicine. 2001;344:1434–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical