A Prospective Multicenter Study Evaluating Learning Curves and Competence in Endoscopic Ultrasound and Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Among Advanced Endoscopy Trainees: The Rapid Assessment of Trainee Endoscopy Skills Study
- PMID: 28625816
- PMCID: PMC7042954
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cgh.2017.06.012
A Prospective Multicenter Study Evaluating Learning Curves and Competence in Endoscopic Ultrasound and Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography Among Advanced Endoscopy Trainees: The Rapid Assessment of Trainee Endoscopy Skills Study
Abstract
Background & aims: On the basis of the Next Accreditation System, trainee assessment should occur on a continuous basis with individualized feedback. We aimed to validate endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) learning curves among advanced endoscopy trainees (AETs) by using a large national sample of training programs and to develop a centralized database that allows assessment of performance in relation to peers.
Methods: ASGE recognized training programs were invited to participate, and AETs were graded on ERCP and EUS exams by using a validated competency assessment tool that assesses technical and cognitive competence in a continuous fashion. Grading for each skill was done by using a 4-point scoring system, and a comprehensive data collection and reporting system was built to create learning curves by using cumulative sum analysis. Individual results and benchmarking to peers were shared with AETs and trainers quarterly.
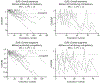
Results: Of the 62 programs invited, 20 programs and 22 AETs participated in this study. At the end of training, median number of EUS and ERCP performed/AET was 300 (range, 155-650) and 350 (125-500), respectively. Overall, 3786 exams were graded (EUS, 1137; ERCP-biliary, 2280; ERCP-pancreatic, 369). Learning curves for individual end points and overall technical/cognitive aspects in EUS and ERCP demonstrated substantial variability and were successfully shared with all programs. The majority of trainees achieved overall technical (EUS, 82%; ERCP, 60%) and cognitive (EUS, 76%; ERCP, 100%) competence at conclusion of training.
Conclusions: These results demonstrate the feasibility of establishing a centralized database to report individualized learning curves and confirm the substantial variability in time to achieve competence among AETs in EUS and ERCP. ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT02509416.
Keywords: Advanced Endoscopy Training; Competence; Competency-based Medical Education; ERCP; EUS; Learning Curves.
Copyright © 2017 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
This author discloses the following: Sachin Wani is supported by the University of Colorado Department of Medicine Outstanding Early Scholars Program and educational grants from Boston Scientific and Cook Medical. The remaining authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures

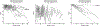

References
-
- Elta GH, Jorgensen J, Coyle WJ. Training in interventional endoscopy: current and future state. Gastroenterology 2015; 148:488–490. - PubMed
-
- Wani S, Keswani R, Elta G, et al. Perceptions of training among program directors and trainees in complex endoscopic procedures (CEPs): a nationwide survey of US ACGME accredited gastroenterology training programs. Gastroenterology 2015; 148:S–150.
-
- Wani S, Hall M, Wang AY, et al. Variation in learning curves and competence for ERCP among advanced endoscopy trainees by using cumulative sum analysis. Gastrointest Endosc 2016; 83:711–719 e11. - PubMed
-
- Wani S, Cote GA, Keswani R, et al. Learning curves for EUS by using cumulative sum analysis: implications for American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy recommendations for training. Gastrointest Endosc 2013;77:558–565. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

