Comparative effects of chronic administrations of gabapentin, pregabalin and baclofen on rat memory using object recognition test
- PMID: 28626478
- PMCID: PMC5465829
- DOI: 10.4103/1735-5362.207201
Comparative effects of chronic administrations of gabapentin, pregabalin and baclofen on rat memory using object recognition test
Abstract
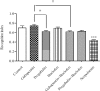
Memory impairment is one of the greatest concerns when it comes to long-term CNS-affecting drug administration. Drugs like gabapentin, pregabalin and baclofen are administered in a long-term period in conditions such as epilepsy, neuropathic pain, spasticity associated with spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis. Despite their wide spread use, few data are available on the effects of these drugs on cognitive functions, such as learning memory. In the present study, the effects of long-term administration of gabapentin, pregabalin and baclofen on memory were investigated in a comparative manner. Male Wistar rats received intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of gabapentin (30 mg/kg), pregabalin (30 mg/kg), baclofen (3 mg/kg), combination of gabapentin/baclofen (30/3 mg/kg) and combination of pregabalin/baclofen (30/3 mg/kg) once a day for 3 weeks respective to their groups. After the end of treatments, rat memories were assessed using the object-recognition task. The discrimination and recognition indices (RI and DI) in the T2 trials were used as the memory indicating factors. The results showed that daily i.p. administrations of pregabalin but not gabapentin or baclofen significantly decreased DI and RI compared to saline group. In combination groups, either gabapentin or pregabalin impaired discrimination between new and familiar objects. Our findings suggested that pregabalin alone or in combination with baclofen significantly caused cognitive deficits.
Keywords: Baclofen; Chronic; Gabapentin; Memory; Object recognition task; Pregabalin.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pregabalin: new drug. Very similar to gabapentin.Prescrire Int. 2005 Dec;14(80):203-6. Prescrire Int. 2005. PMID: 16397976
-
Effect of Gabapentin and Pregabalin in Rat Model of Taxol Induced Neuropathic Pain.J Clin Diagn Res. 2015 May;9(5):FF11-4. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2015/13373.5955. Epub 2015 May 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015. PMID: 26155495 Free PMC article.
-
Use of gabapentin and pregabalin for pruritus and neuropathic pain associated with major burn injury: A retrospective chart review.Burns. 2018 Mar;44(2):414-422. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2017.07.018. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Burns. 2018. PMID: 28822592
-
Pregabalin in neuropathic pain: a more "pharmaceutically elegant" gabapentin?Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2005 Dec;3(4):274-87. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2005. PMID: 16503325 Review.
-
Gabapentin and pregabalin for chronic neuropathic and early postsurgical pain: current evidence and future directions.Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2007 Oct;20(5):456-72. doi: 10.1097/ACO.0b013e3282effaa7. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2007. PMID: 17873599 Review.
Cited by
-
Identifying nootropic drug targets via large-scale cognitive GWAS and transcriptomics.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021 Sep;46(10):1788-1801. doi: 10.1038/s41386-021-01023-4. Epub 2021 May 25. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021. PMID: 34035472 Free PMC article.
-
Spinal cord injury-induced cognitive impairment: a narrative review.Neural Regen Res. 2022 Dec;17(12):2649-2654. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.339475. Neural Regen Res. 2022. PMID: 35662196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of pregabalin on acetic acid-induced colitis in the rats.Res Pharm Sci. 2021 Nov 11;17(1):35-42. doi: 10.4103/1735-5362.329924. eCollection 2022 Feb. Res Pharm Sci. 2021. PMID: 34909042 Free PMC article.
-
Predictors and Interrelationship of Patient-Reported Outcomes in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study.ACR Open Rheumatol. 2023 Jan;5(1):28-37. doi: 10.1002/acr2.11512. Epub 2022 Dec 2. ACR Open Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36461647 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the RMTg Nucleus by Chemogenetic Techniques Alleviates the Learning and Memory Impairment in APP/PS1 Mice.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022 Dec 20;18:2957-2965. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S388832. eCollection 2022. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2022. PMID: 36573138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jensen TS, Baron R, Haanpää M, Kalso E, Loeser JD, Rice AS, et al. A new definition of neuropathic pain. Pain. 2011;152(10):2204–2205. - PubMed
-
- Jensen TS. Anticonvulsants in neuropathic pain: rationale and clinical evidence. Eur J Pain. 2002;6(Suppl A):61–68. - PubMed
-
- Hanna M, O’Brien C, Wilson MC. Prolonged-release oxycodone enhances the effects of existing gabapentin therapy in painful diabetic neuropathy patients. Eur J Pain. 2008;12(6):804–813. - PubMed
-
- Ivanhoe CB, Reistetter TA. Spasticity: the misunderstood part of the upper motor neuron syndrome. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;83(10):S3–S9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

