Validation of three viable-cell counting methods: Manual, semi-automated, and automated
- PMID: 28626709
- PMCID: PMC5466062
- DOI: 10.1016/j.btre.2015.04.004
Validation of three viable-cell counting methods: Manual, semi-automated, and automated
Abstract
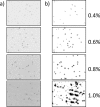
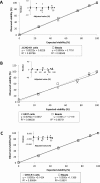
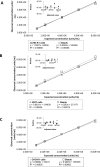
A viable cell count is essential to evaluate the kinetics of cell growth. Since the hemocytometer was first used for counting blood cells, several variants of the methodology have been developed towards reducing the time of analysis and improving accuracy through automation of both sample preparation and counting. The successful implementation of automated techniques relies in the adjustment of cell staining, image display parameters and cell morphology to obtain equivalent precision, accuracy and linearity with respect to the hemocytometer. In this study we conducted the validation of three trypan blue exclusion-based methods: manual, semi-automated, and fully automated; which were used for the estimation of density and viability of cells employed for the biosynthesis and bioassays of recombinant proteins. Our results showed that the evaluated attributes remained within the same range for the automated methods with respect to the manual, providing an efficient alternative for analyzing a huge number of samples.
Keywords: Cell count; Cell viability; Trypan blue exclusion.
Figures

References
-
- Altman A., Randers S., Gonvind R. Comparison of trypan blue dye exclusion and fluorometric assays for mammalian cell viability determinations. Biotechnol. Prog. 1993;9:671–674. - PubMed
-
- Huang L.C., Lin W., Yagami M., Tseng D., Miyashita-Lin E., Singh N., Lin A., Shih S.J. Validation of cell density and viability assays using Cedex automated cell counter. Biologicals. 2010;38:393–400. - PubMed
-
- International Conference on Harmonisation (ICH). Specifications: Test Procedures and Acceptance Criteria for Biotechnological/Biological Products. ICH Harmonised Tripartite Guideline Q 6 B (1999).
-
- Jhonston G. Automated handheld instrument improves counting precision across multiple cell lines. Cell Cult. Technol. 2010;48:325–327.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
