Cohesin Mutations in Myeloid Malignancies
- PMID: 28626802
- PMCID: PMC5472227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.02.006
Cohesin Mutations in Myeloid Malignancies
Abstract
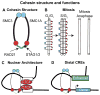
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a hematologic malignancy with a poor prognosis. Recent genome-wide sequencing studies have identified frequent mutations in genes encoding members of the cohesin complex. Mutations in cohesin contribute to myeloid malignancies by conferring enhanced self-renewal of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells but the mechanisms behind this phenotype have not been fully elucidated. Of note, cohesin mutations are highly prevalent in acute megakaryocytic leukemia associated with Down syndrome (DS-AMKL), where they occur in over half of patients. Evidence suggests that cohesin mutations alter gene expression through changes in chromatin accessibility and/or aberrant targeting of epigenetic complexes. In this review we discuss the pathogenic mechanisms by which cohesin mutations contribute to myeloid malignancies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of mutations in the cohesin complex in acute myeloid leukemia.Int J Hematol. 2017 Jan;105(1):31-36. doi: 10.1007/s12185-016-2119-7. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Int J Hematol. 2017. PMID: 27796738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DOT1L inhibitors block abnormal self-renewal induced by cohesin loss.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 31;11(1):7288. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-86646-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33790356 Free PMC article.
-
Cohesin mutations in myeloid malignancies made simple.Curr Opin Hematol. 2018 Mar;25(2):61-66. doi: 10.1097/MOH.0000000000000405. Curr Opin Hematol. 2018. PMID: 29278534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The cohesin subunit Rad21 is a negative regulator of hematopoietic self-renewal through epigenetic repression of Hoxa7 and Hoxa9.Leukemia. 2017 Mar;31(3):712-719. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.240. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Leukemia. 2017. PMID: 27554164 Free PMC article.
-
Cohesin mutations in myeloid malignancies.Blood. 2021 Aug 26;138(8):649-661. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019004259. Blood. 2021. PMID: 34157074 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Topologically Associating Domains and Regulatory Landscapes in Development, Evolution and Disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 6;9:702787. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.702787. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34295901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A cohesive look at leukemogenesis: The cohesin complex and other driving mutations in AML.Neoplasia. 2021 Mar;23(3):337-347. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2021.01.003. Epub 2021 Feb 20. Neoplasia. 2021. PMID: 33621854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Closing the loop on cohesin in hematopoiesis.Blood. 2019 Dec 12;134(24):2123-2125. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019003279. Blood. 2019. PMID: 31830276 Free PMC article.
-
Acute Megakaryocytic Leukemia.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020 Feb 3;10(2):a034884. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a034884. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2020. PMID: 31548219 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MYC: a multipurpose oncogene with prognostic and therapeutic implications in blood malignancies.J Hematol Oncol. 2021 Aug 9;14(1):121. doi: 10.1186/s13045-021-01111-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34372899 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Döhner H, et al. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1136–1152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
