Cohesin Mutations in Myeloid Malignancies
- PMID: 28626802
- PMCID: PMC5472227
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.02.006
Cohesin Mutations in Myeloid Malignancies
Abstract
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) is a hematologic malignancy with a poor prognosis. Recent genome-wide sequencing studies have identified frequent mutations in genes encoding members of the cohesin complex. Mutations in cohesin contribute to myeloid malignancies by conferring enhanced self-renewal of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells but the mechanisms behind this phenotype have not been fully elucidated. Of note, cohesin mutations are highly prevalent in acute megakaryocytic leukemia associated with Down syndrome (DS-AMKL), where they occur in over half of patients. Evidence suggests that cohesin mutations alter gene expression through changes in chromatin accessibility and/or aberrant targeting of epigenetic complexes. In this review we discuss the pathogenic mechanisms by which cohesin mutations contribute to myeloid malignancies.
Figures
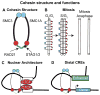
References
-
- Döhner H, et al. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1136–1152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
