Targeted inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress: New hope for renal fibrosis (Review)
- PMID: 28627612
- PMCID: PMC5562070
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6762
Targeted inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress: New hope for renal fibrosis (Review)
Abstract
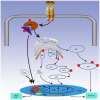
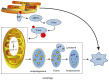
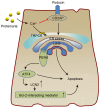
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has a very high mortality rate and remains a global health challenge. Inhibiting renal fibrosis is one of the most promising therapeutic strategies for CKD. Recent studies have indicated that endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) serves an active role in the development of acute and chronic kidney disease, especially with regards to renal fibrosis. In the current review, the authors summarize the latest understanding of the role of ERS during the onset of renal fibrosis. ERS promotes renal fibrosis through multiple signaling pathways, such as transforming growth factor‑β, epithelial‑mesenchymal transition and oxidative stress. In addition, ERS also causes podocyte damage, leading to increased proteinuria and the development of renal fibrosis in rat models. In conclusion, targeted inhibition of ERS may become a promising therapeutic strategy for renal fibrosis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
c‑Jun N‑terminal kinase/transforming growth factor‑β/Smad3 pathway: Is it associated with endoplasmic reticulum stress‑mediated renal interstitial fibrosis?Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jul;20(1):755-762. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10276. Epub 2019 May 22. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31180530
-
Developments in the connection between epithelial‑mesenchymal transition and endoplasmic reticulum stress (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2025 Jul;56(1):102. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5543. Epub 2025 May 9. Int J Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40341397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Cell Death in Renal Fibrosis.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 28;14(8):919. doi: 10.3390/biom14080919. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SREBP-1 Mediates Angiotensin II-Induced TGF-β1 Upregulation and Glomerular Fibrosis.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015 Aug;26(8):1839-54. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013121332. Epub 2014 Nov 14. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25398788 Free PMC article.
-
Renal fibrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics.Kidney Int. 2006 Jan;69(2):213-7. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5000054. Kidney Int. 2006. PMID: 16408108 Review.
Cited by
-
The interaction of S100A16 and GRP78 actives endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated through the IRE1α/XBP1 pathway in renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 13;12(10):942. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04249-8. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34645789 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-185-5p ameliorates endoplasmic reticulum stress and renal fibrosis by downregulation of ATF6.Lab Invest. 2020 Nov;100(11):1436-1446. doi: 10.1038/s41374-020-0447-y. Epub 2020 Jun 8. Lab Invest. 2020. PMID: 32514126
-
Immune cell signatures and inflammatory mediators: unraveling their genetic impact on chronic kidney disease through Mendelian randomization.Clin Exp Med. 2024 May 4;24(1):94. doi: 10.1007/s10238-024-01341-z. Clin Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38703294 Free PMC article.
-
The Active Compounds and Therapeutic Target of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f. in Attenuating Proteinuria in Diabetic Nephropathy: A Review.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Sep 21;8:747922. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.747922. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34621768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Treating Renal Interstitial Fibrosis via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Mediated Apoptosis.Biomed Res Int. 2021 May 15;2021:6667791. doi: 10.1155/2021/6667791. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34055995 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

