Involvement of the glutamate/glutamine cycle and glutamate transporter GLT-1 in antidepressant-like effects of Xiao Yao san on chronically stressed mice
- PMID: 28629384
- PMCID: PMC5477120
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1830-0
Involvement of the glutamate/glutamine cycle and glutamate transporter GLT-1 in antidepressant-like effects of Xiao Yao san on chronically stressed mice
Retraction in
-
Retraction Note: Involvement of the glutamate/glutamine cycle and glutamate transporter GLT-1 in antidepressant-like effects of Xiao Yao san on chronically stressed mice.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Jul 15;23(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04089-3. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37454052 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Xiao Yao San (XYS) is an herbal prescription which is used in the treatment of depression for thousands of years from Song dynasty in China (960-1127 A.D.), and is the bestselling and most popular herb formula for treating major depression. This study aimed to assess the chronic antidepressant effects of XYS and fluoxetine in depressed mice induced by chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) and its association with alterations in glutamate/glutamine cycle and glutamate transporters.
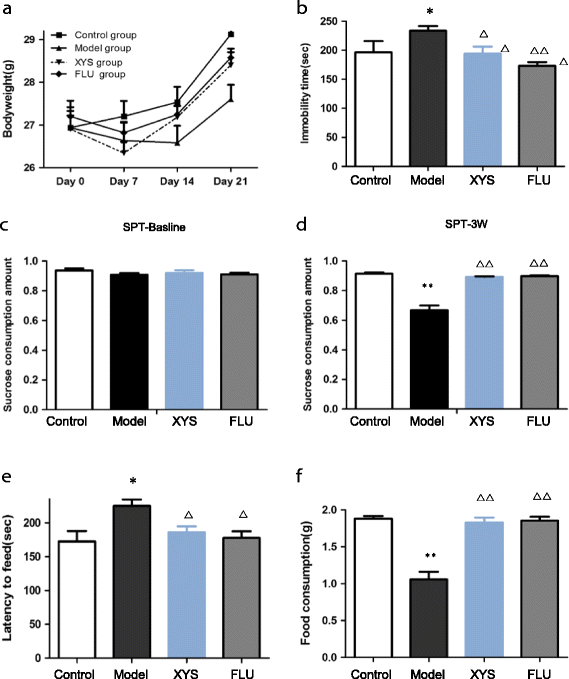
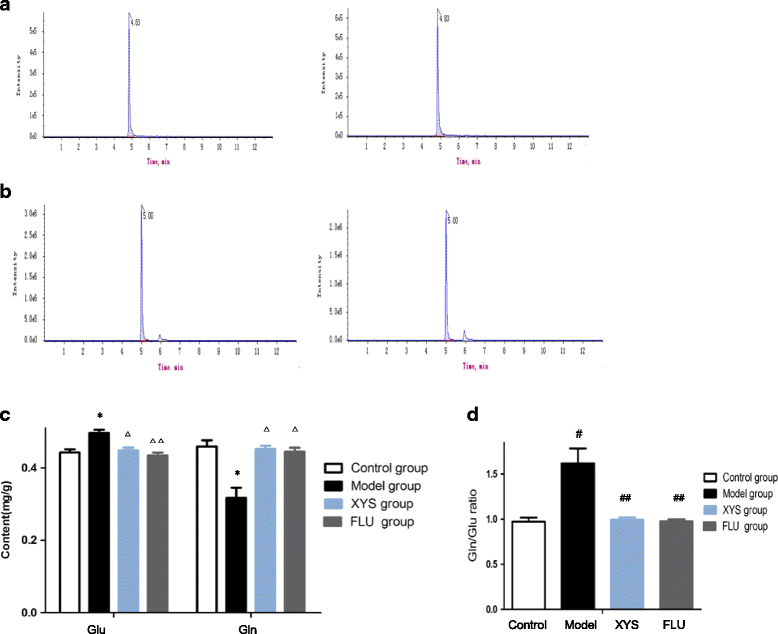
Methods: Mice in the control and model group were given 0.5 ml physiological saline by intragastric administration. Mice in two treatment groups were given XYS (0.25 g/kg/d) and fluoxetine (2.6 mg/kg/d), respectively. The depressive-like behaviors such as forced swim test (FST), sucrose preference test (SPT) and novelty-suppressed feeding (NSF) test were measured after mice exposed to CUMS for 21 days. Body weight, contents of glutamate and glutamine, glutamine/glutamate ratio that is usually thought to reflect glutamate/glutamine cycle, and the protein and mRNA expressions of glutamate transporters (excitatory amino acid transporter 1-2,GLAST/EAAT1 and GLT-1/EAAT2) were measured. The immunoreactivities of GLAST and GLT-1 in the hippocampus were also investigated.
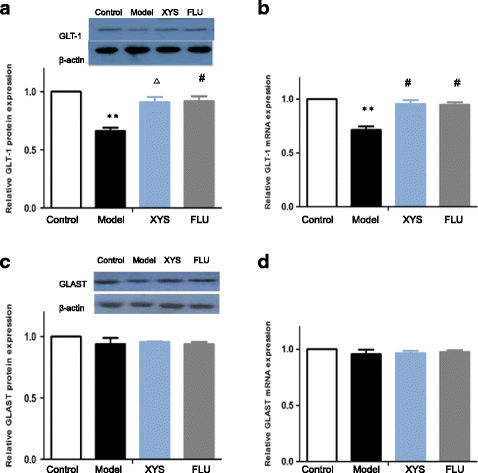
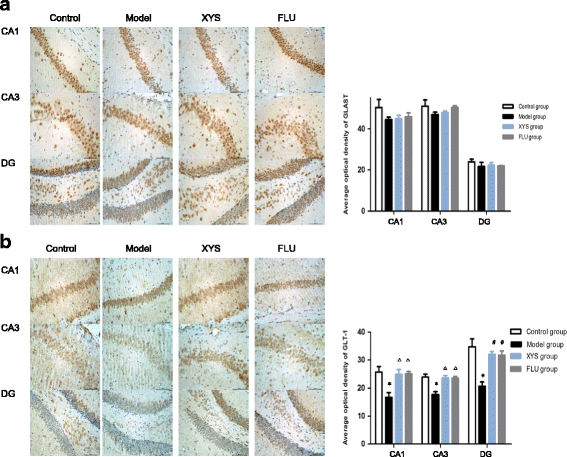
Results: After CUMS exposure, mice exhibited depressive-like behaviors, body weight loss, increased glutamate level, decreased glutamine level, elevated glutamine/glutamate ratio, decreased GLT-1 protein expression and mRNA level, and decreased average optical density (AOD) of GLT-1 in the CA1, CA3 and DG in the hippocampus. These abnormalities could be effectively reversed by XYS or fluoxetine treatment. In addition, the study also found that GLAST expression in the hippocampus could not be altered by 21-d CUMS.
Conclusion: The studies indicated that XYS may have therapeutic actions on depression -like behavior s induced by CUMS in mice possibly mediated by modulation of glutamate/glutamine cycle and glutamate transporter GLT-1 in the hippocampus.
Keywords: Animal research; Depression; Herbal medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Xiaoyaosan exerts antidepressant-like effects by regulating the functions of astrocytes and EAATs in the prefrontal cortex of mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019 Aug 14;19(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12906-019-2613-6. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2019. Retraction in: BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Jan 16;25(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04757-6. PMID: 31412844 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Studies on the potential link between antidepressant effect of Xiaoyao San and its pharmacological activity of hepatoprotection based on multi-platform metabolomics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Mar 1;249:112432. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2019.112432. Epub 2019 Nov 29. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31790818
-
Involvement of the astroglial glutamate-glutamine cycle in the analgesic effects of electroacupuncture in a rat model of chronic neuropathic pain.Acupunct Med. 2025 Feb;43(1):14-25. doi: 10.1177/09645284241309952. Epub 2024 Dec 30. Acupunct Med. 2025. PMID: 39912444
-
The role of astrocytic glutamate transporters GLT-1 and GLAST in neurological disorders: Potential targets for neurotherapeutics.Neuropharmacology. 2019 Dec 15;161:107559. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.03.002. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Neuropharmacology. 2019. PMID: 30851309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Astrocyte control of glutamatergic activity: Downstream effects on serotonergic function and emotional behavior.Neuropharmacology. 2020 Apr;166:107914. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107914. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Neuropharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32045742 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Xiaoyaosan on Colon Morphology and Intestinal Permeability in Rats With Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Jul 16;11:1069. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01069. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32765272 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and biochemical imaging reveals systemic LPS-induced changes in the rat brain.J Neuroimmunol. 2020 Nov 15;348:577367. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2020.577367. Epub 2020 Aug 26. J Neuroimmunol. 2020. PMID: 32866714 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Histone Modification in Major Depressive Disorder.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022;20(7):1261-1277. doi: 10.2174/1570159X19666210922150043. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34551699 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of Hepatic SHIP2 and PI3K/Akt Signalling in the Regulation of Plasma Insulin by Xiaoyaosan in Chronic Immobilization-Stressed Rats.Molecules. 2019 Jan 29;24(3):480. doi: 10.3390/molecules24030480. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 30699999 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Stress in a Rat Model of Depression Disturbs the Glutamine-Glutamate-GABA Cycle in the Striatum, Hippocampus, and Cerebellum.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020 Feb 24;16:557-570. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S245282. eCollection 2020. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020. PMID: 32158215 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mathers C, Fat DM, Boerma J. The global burden of disease: 2004 update: World Health Organization. 2008.
-
- American PA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5®): American psychiatric pub. 2013. - PubMed
-
- Verhoof E, Maurice-Stam H, Heymans H, Grootenhuis M. Health-related quality of life, anxiety and depression in young adults with disability benefits due to childhood-onset somatic conditions. Child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health. 2013;7:12–21. doi: 10.1186/1753-2000-7-12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

