Reduction of breathing irregularity-related motion artifacts in low-pitch spiral 4D CT by optimized projection binning
- PMID: 28629434
- PMCID: PMC5477247
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-017-0835-7
Reduction of breathing irregularity-related motion artifacts in low-pitch spiral 4D CT by optimized projection binning
Abstract
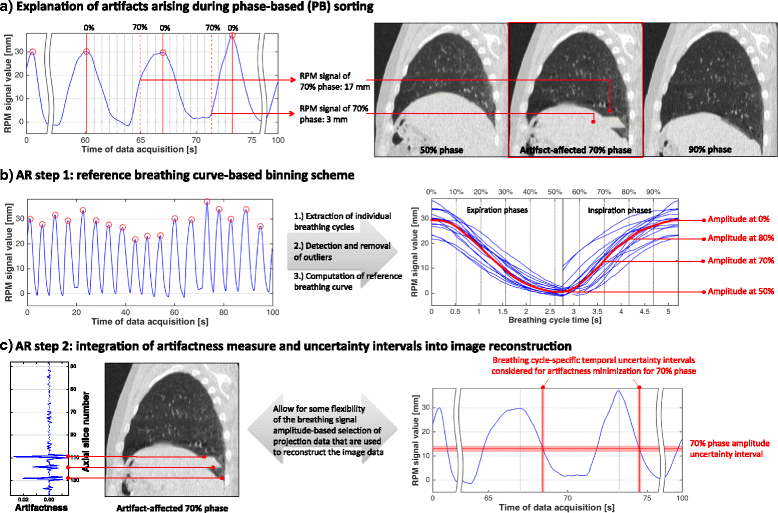
Background: Respiration-correlated CT (4D CT) is the basis of radiotherapy treatment planning of thoracic and abdominal tumors. Current clinical 4D CT images suffer, however, from artifacts due to unfulfilled assumptions concerning breathing pattern regularity. We propose and evaluate modifications to existing low-pitch spiral 4D CT reconstruction protocols to counteract respective artifacts.
Methods: The proposed advanced reconstruction (AR) approach consists of two steps that build on each other: (1) statistical analysis of the breathing signal recorded during CT data acquisition and extraction of a patient-specific reference breathing cycle for projection binning; (2) incorporation of an artifact measure into the reconstruction. 4D CT data of 30 patients were reconstructed by standard phase- and local amplitude-based reconstruction (PB, LAB) and compared with images obtained by AR. The number of artifacts was evaluated and artifact statistics correlated to breathing curve characteristics.
Results: AR reduced the number of 4D CT artifacts by 31% and 27% compared to PB and LAB; the reduction was most pronounced for irregular breathing curves.
Conclusions: We described a two-step optimization of low-pitch spiral 4D CT reconstruction to reduce artifacts in the presence of breathing irregularity and illustrated that the modifications to existing reconstruction solutions are effective in terms of artifact reduction.
Keywords: 4D CT; Artifact reduction; Breathing irregularity; Motion artifacts.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

