The small GTPases K-Ras, N-Ras, and H-Ras have distinct biochemical properties determined by allosteric effects
- PMID: 28630043
- PMCID: PMC5546037
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.778886
The small GTPases K-Ras, N-Ras, and H-Ras have distinct biochemical properties determined by allosteric effects
Abstract
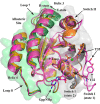
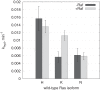
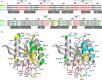
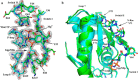
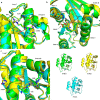
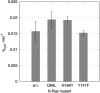
H-Ras, K-Ras, and N-Ras are small GTPases that are important in the control of cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival, and their mutants occur frequently in human cancers. The G-domain, which catalyzes GTP hydrolysis and mediates downstream signaling, is 95% conserved between the Ras isoforms. Because of their very high sequence identity, biochemical studies done on H-Ras have been considered representative of all three Ras proteins. We show here that this is not a valid assumption. Using enzyme kinetic assays under identical conditions, we observed clear differences between the three isoforms in intrinsic catalysis of GTP by Ras in the absence and presence of the Ras-binding domain (RBD) of the c-Raf kinase protein (Raf-RBD). Given their identical active sites, isoform G-domain differences must be allosteric in origin, due to remote isoform-specific residues that affect conformational states. We present the crystal structure of N-Ras bound to a GTP analogue and interpret the kinetic data in terms of structural features specific for H-, K-, and N-Ras.
Keywords: Ras protein; allosteric regulation; conformational change; enzyme catalysis; enzyme structure; oncogene.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
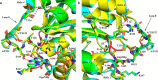
References
-
- Hancock J. F. (2003) Ras proteins: different signals from different locations. Nature reviews. Mol. Cell Biol. 4, 373–384 - PubMed
-
- Milburn M. V., Tong L., deVos A. M., Brünger A., Yamaizumi Z., Nishimura S., and Kim S. H. (1990) Molecular switch of signal transduction: structural differences between active and inactive forms of protooncogenic ras proteins. Science 247, 939–945 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

