Apoptotic foci at mitochondria: in and around Bax pores
- PMID: 28630156
- PMCID: PMC5483519
- DOI: 10.1098/rstb.2016.0217
Apoptotic foci at mitochondria: in and around Bax pores
Abstract
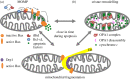
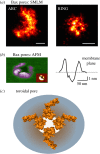
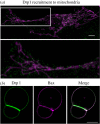
The permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane by Bax and Bak during apoptosis is considered a key step and a point of no return in the signalling pathway. It is always closely related to the reorganization of mitochondrial cristae that frees cytochrome c to the intermembrane space and to massive mitochondrial fragmentation mediated by the dynamin-like protein Drp1. Despite multiple evidence in favour of a functional link between these processes, the molecular mechanisms that connect them and their relevance for efficient apoptosis signalling remain obscure. In this review, we discuss recent progress on our understanding of how Bax forms pores in the context of Drp1-stabilized signalling platforms at apoptotic foci in mitochondria.This article is part of the themed issue 'Membrane pores: from structure and assembly, to medicine and technology'.
Keywords: Bcl-2; MOMP; cristae remodelling; membrane curvature; mitochondrial fragmentation.
© 2017 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
We declare we have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
