Genome Evolution to Penicillin Resistance in Serotype 3 Streptococcus pneumoniae by Capsular Switching
- PMID: 28630198
- PMCID: PMC5571339
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00478-17
Genome Evolution to Penicillin Resistance in Serotype 3 Streptococcus pneumoniae by Capsular Switching
Abstract
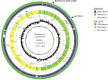
Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates of serotype 3 were collected from cases of invasive pneumococcal disease (n = 124) throughout Japan between April 2010 and March 2013. A penicillin-resistant S. pneumoniae (PRSP) isolate from an adult patient, strain KK0981 of serotype 3, was identified among these strains. Whole-genome analysis characterized this PRSP as a recombinant strain derived from PRSP of serotype 23F with the cps locus (20.3 kb) replaced by that of a penicillin-susceptible strain of serotype 3.
Keywords: Streptococcus pneumoniae; capsular switching; gPRSP; serotype 3.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine on Genotypic Penicillin Resistance and Serotype Changes, Japan, 2010-2017.Emerg Infect Dis. 2018 Nov;24(11):2010-2020. doi: 10.3201/eid2411.180326. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30334707 Free PMC article.
-
High Rate of Serotype Switching and Genetic Variations Indicates Widespread Recombination Between Clinical and Commensal Penicillin-Nonsusceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae in Tehran.Microb Drug Resist. 2019 Jul/Aug;25(6):865-873. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2018.0336. Epub 2019 Feb 20. Microb Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 30785836
-
Molecular epidemiological characterization in mucoid-type Streptococcus pneumoniae isolates obtained from invasive pneumococcal disease patients in Japan.J Infect Chemother. 2021 Feb;27(2):211-217. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2020.09.014. Epub 2020 Sep 29. J Infect Chemother. 2021. PMID: 33004265
-
Decoding the Penicillin Resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae for Invasive and Noninvasive Infections.Microb Drug Resist. 2021 Jul;27(7):942-950. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2020.0233. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Microb Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 32996825 Review.
-
Bacterial gene transfer by natural genetic transformation.APMIS Suppl. 1998;84:43-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.1998.tb05647.x. APMIS Suppl. 1998. PMID: 9850681 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Conquering the pneumococcal nemesis with oral antibiotics.J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2020 Feb 10;10(1):65-68. doi: 10.1080/20009666.2019.1708637. eCollection 2020. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. 2020. PMID: 32128062 Free PMC article.
-
Streptococcus pneumoniae serotype 3 genotypes in invasive isolates from Colombia.Biomedica. 2021 Jun 29;41(2):338-346. doi: 10.7705/biomedica.5407. Biomedica. 2021. PMID: 34214273 Free PMC article.
-
Genomics and Genetics of Streptococcus pneumoniae.Microbiol Spectr. 2019 May;7(3):10.1128/microbiolspec.gpp3-0025-2018. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.GPP3-0025-2018. Microbiol Spectr. 2019. PMID: 31111814 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine on Genotypic Penicillin Resistance and Serotype Changes, Japan, 2010-2017.Emerg Infect Dis. 2018 Nov;24(11):2010-2020. doi: 10.3201/eid2411.180326. Emerg Infect Dis. 2018. PMID: 30334707 Free PMC article.
-
PspA Diversity, Serotype Distribution and Antimicrobial Resistance of Invasive Pneumococcal Isolates from Paediatric Patients in Shenzhen, China.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Jan 11;14:49-58. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S286187. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 33469319 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chiba N, Morozumi M, Shouji M, Wajima T, Iwata S, Sunakawa K, Ubukata K; Invasive Pneumococcal Diseases Surveillance Study Group. 2013. Invasive Pneumococcal Diseases Surveillance Study Group. Rapid decrease of 7-valent conjugate vaccine coverage for invasive pneumococcal diseases in pediatric patients in Japan. Microb Drug Resist 19:308–315. doi:10.1089/mdr.2012.0180. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chiba N, Morozumi M, Shouji M, Wajima T, Iwata S, Ubukata K; Invasive Pneumococcal Diseases Surveillance Study Group. 2014. Changes in capsule and drug resistance of peumococci after introduction of PCV7, Japan, 2010-2013. Emerg Infect Dis 20:1132–1139. doi:10.3201/eid2007.131485. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ubukata K, Chiba N, Hanada S, Morozumi M, Wajima T, Shouji M, Iwata S; Invasive Pneumococcal Diseases Surveillance Study Group. 2015. Serotype changes and drug resistance in invasive pneumococcal diseases in adults after vaccinations in children, Japan, 2010-2013. Emerg Infect Dis 21:1956–1965. doi:10.3201/eid2111.142029. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Harboe ZB, Dalby T, Weinberger DM, Benfield T, Mølbak K, Slotved HC, Suppli CH, Konradsen HB, Valentiner-Branth P. 2014. Impact of 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccination in invasive pneumococcal disease incidence and mortality. Clin Infect Dis 59:1066–1073. doi:10.1093/cid/ciu524. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

