Recent Advances in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Toxicities With Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibition
- PMID: 28630211
- PMCID: PMC5509510
- DOI: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.08856
Recent Advances in Hypertension and Cardiovascular Toxicities With Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Inhibition
Abstract
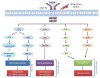
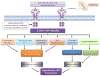
Physiologically, vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) and their receptors (VEGFR) play a critical role in vascular development, neogenesis, angiogenesis, endothelial function and vascular tone. Pathologically, VEGF-VEGFR signaling induces dysregulated angiogenesis, which contributes to the growth and spread of tumors. The development of VEGF-VEGFR inhibitors (VEGFIs) has thus proven to be a valuable strategy in the management of a number of malignancies, yielding improved survival outcomes. Not surprisingly, VEGFIs are now standard of care as first-line monotherapy for some cancers and the scope of this class of drugs is growing. However with the promise of improved outcomes, VEGFIs also led to clinically relevant toxicities, especially hypertension and cardiovascular disease (CVD). As such, cancer patients treated with VEGFIs may have improved cancer outcomes, but at the cost of an increased risk of CVD. Indeed, dose intensity and protracted use of these drugs can be limited by cardiovascular side effects and patients may require dose reduction or drug withdrawal, thus compromising anti-cancer efficacy and survival. Here we summarize the vascular biology of VEGF-VEGFR signaling and discuss the cardiovascular consequences and clinical impact of VEGFIs. New insights into molecular mechanisms whereby VEGFIs cause hypertension and heart disease are highlighted.
Figures
References
-
- Simons M, Gordon E, Claesson-Welsh L. Mechanisms and regulation of endothelial VEGF receptor signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2016;17:611–625. - PubMed
-
- Gordon EJ, Fukuhara D, Weström S, Padhan N, Sjöström EO, van Meeteren L, He L, Orsenigo F, Dejana E, Bentley K, Spurkland A, Claesson-Welsh L. The endothelial adaptor molecule TSAd is required for VEGF-induced angiogenic sprouting through junctional c-Src activation. Sci Signal. 2016;9:ra72. - PubMed
-
- Yogi A, Callera GE, Aranha AB, Graham D, McBride MW, Dominiczak AF, Touyz RM. Sphingosine-1-phosphate-induced inflammation involves receptor tyrosine kinase transactivation in vascular cells: upregulation in hypertension. Hypertension. 2011;57:809–818. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

